Therapeutic management of classic lichen planopilaris: a systematic review
- PMID: 29520159
- PMCID: PMC5833781
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S137870
Therapeutic management of classic lichen planopilaris: a systematic review
Abstract
Several treatment strategies have been proposed in classic lichen planopilaris (LPP), although no gold standard therapeutic approach has been recognized so far due to the variable and, sometimes, contradictory results reported in the literature, as well as due to the lack of guidelines and randomized controlled trials. In the present review, we sought to provide an updated overview on the treatment of classic LPP by analyzing the level of evidence of published studies, also proposing a possible therapeutic strategy according to the findings highlighted in this systematic review.
Keywords: lichen planopilaris; management; therapy; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
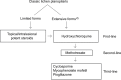
References
-
- Lyakhovitsky A, Amichai B, Sizopoulou C, Barzilai A. A case series of 46 patients with lichen planopilaris: demographics, clinical evaluation, and treatment experience. J Dermatolog Treat. 2015;26(3):275–279. - PubMed
-
- Assouly P, Reigagne P. Lichen planopilaris: update on diagnosis and treatment. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2009;28(1):3–10. - PubMed
-
- Rácz E, Gho C, Moorman PW, Noordhoek Hegt V, Neumann HA. Treatment of frontal fibrosing alopecia and lichen planopilaris: a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27(12):1461–1470. - PubMed
-
- Piguet V, Breathnach SM, Le Cleach L. Lichen planus and lichenoid disorders. In: Griffiths CEM, Barker J, Bleiker T, Chalmers R, Creamer D, editors. Rook’s Textbook of Dermatology. 9th ed. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell; 2016. pp. 37.6–37.7.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

