Acute Down-regulation of BDNF Signaling Does Not Replicate Exacerbated Amyloid-β Levels and Cognitive Impairment Induced by Cholinergic Basal Forebrain Lesion
- PMID: 29520217
- PMCID: PMC5827359
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00051
Acute Down-regulation of BDNF Signaling Does Not Replicate Exacerbated Amyloid-β Levels and Cognitive Impairment Induced by Cholinergic Basal Forebrain Lesion
Abstract
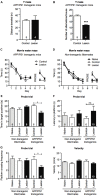
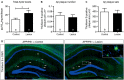
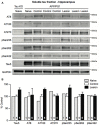
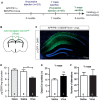
Degeneration of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons (BFCNs) precedes hippocampal degeneration and pathological amyloid-beta (Aβ) accumulation, and underpins the development of cognitive dysfunction in sporadic Alzheimer's disease (AD). We hypothesized that degeneration of BFCNs causes a decrease in neurotrophin levels in innervated brain areas, which in turn promotes the development of Aβ pathology and cognitive impairment. Here we show that lesion of septo-hippocampal BFCNs in a pre-symptomatic transgenic amyloid AD mouse model (APP/PS1 mice) increases soluble Aβ levels in the hippocampus, and induces cognitive deficits in a spatial memory task that are not seen in either unlesioned APP/PS1 or non-transgenic littermate control mice. Furthermore, the BFCN lesion results in decreased levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). However, viral knockdown of neuronal BDNF in the hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice (in the absence of BFCN loss) neither increased the level of Aβ nor caused cognitive deficits. These results suggest that the cognitive decline and Aβ pathology induced by BFCN loss occur independent of dysfunctional neuronal BDNF signaling, and may therefore be directly underpinned by reduced cholinergic neurotransmission.
Keywords: APP/PS1 transgenic mouse; Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid-β; basal forebrain; brain-derived neurotrophic factor; cholinergic neuron.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cholinergic Basal Forebrain Lesion Decreases Neurotrophin Signaling without Affecting Tau Hyperphosphorylation in Genetically Susceptible Mice.J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;55(3):1141-1154. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160805. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 27767994
-
Chemical genetic activation of the cholinergic basal forebrain hippocampal circuit rescues memory loss in Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2022 Apr 13;14(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s13195-022-00994-w. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35418161 Free PMC article.
-
Cholinergic degeneration is associated with increased plaque deposition and cognitive impairment in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice.Behav Brain Res. 2013 Mar 1;240:146-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2012.11.012. Epub 2012 Nov 22. Behav Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23178660
-
NGF and the Amyloid Precursor Protein in Alzheimer's Disease: From Molecular Players to Neuronal Circuits.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1331:145-165. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-74046-7_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34453297 Review.
-
Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Neurons: Linking Down Syndrome and Alzheimer's Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Jul 12;13:703876. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.703876. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34322015 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease: An Educational Literature Review.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jun;62(6):6785-6810. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04468-y. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39254911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholinergic basal forebrain degeneration due to sleep-disordered breathing exacerbates pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 2;13(1):6543. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33624-y. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36323689 Free PMC article.
-
Hypocretin/orexin influences chronic sleep disruption injury in the hippocampus.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Oct 6;14:1025402. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1025402. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36275002 Free PMC article.
-
Removal of p75 Neurotrophin Receptor Expression from Cholinergic Basal Forebrain Neurons Reduces Amyloid-β Plaque Deposition and Cognitive Impairment in Aged APP/PS1 Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Jul;56(7):4639-4652. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1404-2. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30374941
-
Neuroprotective role of Diosgenin, a NGF stimulator, against Aβ (1-42) induced neurotoxicity in animal model of Alzheimer's disease.Metab Brain Dis. 2022 Feb;37(2):359-372. doi: 10.1007/s11011-021-00880-8. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Metab Brain Dis. 2022. PMID: 35023028
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

