α-Synuclein Heterocomplexes with β-Amyloid Are Increased in Red Blood Cells of Parkinson's Disease Patients and Correlate with Disease Severity
- PMID: 29520218
- PMCID: PMC5827358
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00053
α-Synuclein Heterocomplexes with β-Amyloid Are Increased in Red Blood Cells of Parkinson's Disease Patients and Correlate with Disease Severity
Abstract
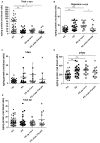
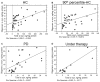
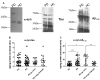
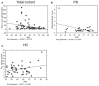
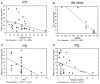
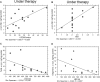
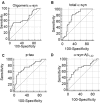
Neurodegenerative disorders (NDs) are characterized by abnormal accumulation/misfolding of specific proteins, primarily α-synuclein (α-syn), β-amyloid1-42 (Aβ1-42) and tau, in both brain and peripheral tissues. In addition to oligomers, the role of the interactions of α-syn with Aβ or tau has gradually emerged. Nevertheless, despite intensive research, NDs have no accepted peripheral markers for biochemical diagnosis. In this respect, Red Blood Cells (RBCs) are emerging as a valid peripheral model for the study of aging-related pathologies. Herein, a small cohort (N = 28) of patients affected by Parkinson's disease (PD) and age-matched controls were enrolled to detect the content of α-syn (total and oligomeric), Aβ1-42 and tau (total and phosphorylated) in RBCs. Moreover, the presence of α-syn association with tau and Aβ1-42 was explored by co-immunoprecipitation/western blotting in the same cells, and quantitatively confirmed by immunoenzymatic assays. For the first time, PD patients were demonstrated to exhibit α-syn heterocomplexes with Aβ1-42 and tau in peripheral tissues; interestingly, α-syn-Aβ1-42 concentrations were increased in PD subjects with respect to healthy controls (HC), and directly correlated with disease severity and motor deficits. Moreover, total-α-syn levels were decreased in PD subjects and inversely related to their motor deficits. Finally, an increase of oligomeric-α-syn and phosphorylated-tau was observed in RBCs of the enrolled patients. The combination of three parameters (total-α-syn, phosphorylated-tau and α-syn-Aβ1-42 concentrations) provided the best fitting predictive index for discriminating PD patients from controls. Nevertheless further investigations should be required, overall, these data suggest α-syn hetero-aggregates in RBCs as a putative tool for the diagnosis of PD.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; neurodegenerative disorders; tau; α-synuclein; α-synuclein heterocomplexes; β-amyloid.
Figures
References
-
- Abd-Elhadi S., Honig A., Simhi-Haham D., Schechter M., Linetsky E., Ben-Hur T., et al. . (2015). Total and proteinase K-resistant α-synuclein levels in erythrocytes, determined by their ability to bind phospholipids, associate with Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 5:11120. 10.1038/srep11120 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alves G., Brønnick K., Aarsland D., Blennow K., Zetterberg H., Ballard C., et al. . (2010). CSF amyloid-β and tau proteins and cognitive performance, in early and untreated Parkinson’s disease: the Norwegian ParkWest study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 81, 1080–1086. 10.1136/jnnp.2009.199950 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

