A Computational Assessment of Target Engagement in the Treatment of Auditory Hallucinations with Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation
- PMID: 29520240
- PMCID: PMC5826940
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00048
A Computational Assessment of Target Engagement in the Treatment of Auditory Hallucinations with Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation
Abstract
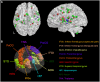
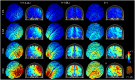
We use auditory verbal hallucinations (AVH) to illustrate the challenges in defining and assessing target engagement in the context of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for psychiatric disorders. We defined the target network as the cluster of regions of interest (ROIs) that are consistently implicated in AVH based on the conjunction of multimodal meta-analytic neuroimaging data. These were prescribed in the New York Head (a population derived model) and head models of four single individuals. We appraised two potential measures of target engagement, tDCS-induced peak electric field strength and tDCS-modulated volume defined as the percentage of the volume of the AVH network exposed to electric field magnitude stronger than the postulated threshold for neuronal excitability. We examined a left unilateral (LUL) montage targeting the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and temporoparietal junction (TPJ), a bilateral (BL) prefrontal montage, and a 2 × 1 montage targeting the left PFC and the TPJ bilaterally. Using computational modeling, we estimated the peak electric field strength and modulated volume induced by each montage for current amplitudes ranging 1-4 mA. We found that the LUL montage was inferior to both other montages in terms of peak electric field strength in right-sided AVH-ROIs. The BL montage was inferior to both other montages in terms of modulated volume of the left-sided AVH-ROIs. As the modulated volume is non-linear, its variability between montages reduced for current amplitudes above 3 mA. These findings illustrate how computational target engagement for tDCS can be tailored to specific networks and provide a principled approach for future study design.
Keywords: auditory hallucinations; computational modeling; neuroimaging; schizophrenia; transcranial direct current stimulation.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

