Metabolic Modulation in Macrophage Effector Function
- PMID: 29520272
- PMCID: PMC5827535
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00270
Metabolic Modulation in Macrophage Effector Function
Abstract
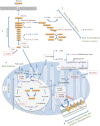
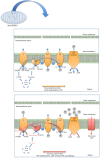
Traditionally cellular respiration or metabolism has been viewed as catabolic and anabolic pathways generating energy and biosynthetic precursors required for growth and general cellular maintenance. However, growing literature provides evidence of a much broader role for metabolic reactions and processes in controlling immunological effector functions. Much of this research into immunometabolism has focused on macrophages, cells that are central in pro- as well as anti-inflammatory responses-responses that in turn are a direct result of metabolic reprogramming. As we learn more about the precise role of metabolic pathways and pathway intermediates in immune function, a novel opportunity to target immunometabolism therapeutically has emerged. Here, we review the current understanding of the regulation of macrophage function through metabolic remodeling.
Keywords: electron transport chain; glycolysis; immunometabolism; macrophage; tricarboxylic acid cycle.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

