The Influence of Invariant Natural Killer T Cells on Humoral Immunity to T-Dependent and -Independent Antigens
- PMID: 29520280
- PMCID: PMC5827355
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00305
The Influence of Invariant Natural Killer T Cells on Humoral Immunity to T-Dependent and -Independent Antigens
Abstract
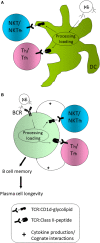
Vaccination with CD1d-binding glycolipid adjuvants and co-administered protein, lipid, and carbohydrate antigens leads to invariant natural killer T (NKT) cell-dependent enhancement of protective B cell responses. NKT cell activation boosts the establishment of protein antigen-specific B cell memory and long-lived plasma cell (LLPC) compartments. NKT cells may exert a similar effect on some carbohydrate-specific B cells, but not lipid-specific B cells. The mechanisms of action of NKT cells on B cell responsiveness and subsequent differentiation into memory B cells and LLPC is dependent on CD1d expression by dendritic cells and B cells that can co-present glycolipids on CD1d and antigen-derived peptide on MHCII. CD1d/glycolipid-activated NKT cells are able to provide help to B cells in a manner dependent on cognate and non-cognate interactions. More recently, a glycolipid-expanded subset of IL-21-secreting NKT cells known as NKT follicular helper cells has been suggested to be a driver of NKT-enhanced humoral immunity. This review summarizes established and recent findings on how NKT cells impact humoral immunity and suggests possible areas of investigation that may allow the incorporation of NKT-activating agents into vaccine adjuvant platforms.
Keywords: CD1d; Natural Killer T; humoral immunity; pathogen; vaccine.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

