Early disseminated recurrence after liver resection in solitary hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 29520346
- PMCID: PMC5842084
- DOI: 10.4174/astr.2018.94.3.129
Early disseminated recurrence after liver resection in solitary hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Although few hepatectomy patients develop unexpected early diffuse and multinodular recurrence in the remnant liver, the prognosis in such cases is often dismal. The aim of this study was to evaluate the risk factors of early disseminated multinodular hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) recurrence within 3 months after liver resection for solitary HCC.
Methods: Eighty-four patients who were diagnosed with recurrent HCC within 3 months after hepatectomy for solitary HCC were retrospectively reviewed. Disseminated HCC recurrence was defined as more than 10 tumors in both lobes and total tumor size >10 cm.
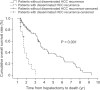
Results: Preoperative α-FP level, incidence of poor tumor grade, and presence of portal vein tumor thrombosis were higher in the patients with disseminated HCC recurrence than in those without disseminated HCC recurrence (P < 0.05). Multivariate analysis showed that α-FP >1,000 ng/dL was a predisposing factor of disseminated HCC recurrence within 3 months after liver resection. The overall survival rate for patients without disseminated HCC recurrence was higher than that for patients with disseminated HCC recurrence (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Early disseminated multinodular HCC recurrence in hepatectomy patients was associated with preoperative α-FP >1,000 ng/dL. Such patients should be frequently evaluated for the early detection of recurrent HCC for early intervention.
Keywords: Hepatectomy; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Recurrence; Survival; Tumor biomarker.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Cherqui D, Laurent A, Mocellin N, Tayar C, Luciani A, Van Nhieu JT, et al. Liver resection for transplantable hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term survival and role of secondary liver transplantation. Ann Surg. 2009;250:738–746. - PubMed
-
- Lee HY, Rhim H, Lee MW, Kim YS, Choi D, Park MJ, et al. Early diffuse recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation: analysis of risk factors. Eur Radiol. 2013;23:190–197. - PubMed
-
- Kim JM, Kwon CH, Joh JW, Park JB, Lee JH, Kim SJ, et al. Outcomes after curative hepatectomy in patients with non-B non-C hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus hepatocellular carcinoma from non-cirrhotic liver. J Surg Oncol. 2014;110:976–981. - PubMed
-
- Kim JM, Kwon CH, Joh JW, Park JB, Lee JH, Kim SJ, et al. Differences between hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus infection in patients with and without cirrhosis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21:458–465. - PubMed
-
- Imamura H, Matsuyama Y, Tanaka E, Ohkubo T, Hasegawa K, Miyagawa S, et al. Risk factors contributing to early and late phase intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. J Hepatol. 2003;38:200–207. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources