Delineation between different components of chronic pain using dimension reduction - an ASL fMRI study in hand osteoarthritis
- PMID: 29520913
- PMCID: PMC6055802
- DOI: 10.1002/ejp.1212
Delineation between different components of chronic pain using dimension reduction - an ASL fMRI study in hand osteoarthritis
Abstract
Background: Traditional psychometric measures aimed at characterizing the pain experience often show considerable overlap, due to interlinked affective and modulatory processes under central nervous system control. Neuroimaging studies have been employed to investigate this complexity of pain processing, in an attempt to provide a quantifiable, adjunctive description of pain perception. In this exploratory study, we examine psychometric and neuroimaging data from 38 patients with painful osteoarthritis of the carpometacarpal joint. We had two aims: first, to utilize principal component analysis (PCA) as a dimension reduction strategy across multiple self-reported endpoints of pain, cognitive and affective functioning; second, to investigate the relationship between identified dimensions and regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) as an indirect measure of brain activity underpinning their ongoing pain experiences.
Methods: Psychometric data were collected using validated questionnaires. Quantitative estimates of rCBF were acquired using pseudo-continuous arterial spin-labelled functional magnetic resonance imaging.
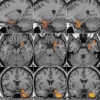
Results: Two principal components were identified that accounted for 73% of data variance; one related to pain scores and a second to psychological traits. Voxel-wise multiple regression analysis revealed a significant negative association between the 'pain score' component and rCBF to a right temporal lobe cluster, including the amygdala and the parahippocampal cortex.
Conclusion: We suggest this association may represent a coping mechanism that aims to reduce fear-related pain-anxiety. Further investigation of central brain processing mechanisms in osteoarthritis-related pain may offer insights into more effective therapeutic strategies.
Significance: This study demonstrates that dimension reduction using PCA allows insight into pain perception and its affective components in relation to brain activation patterns in patients with painful hand osteoarthritis.
© 2018 The Authors. European Journal of Pain published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Pain Federation - EFIC®.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Alterations in resting-state regional cerebral blood flow demonstrate ongoing pain in osteoarthritis: An arterial spin-labeled magnetic resonance imaging study.Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Dec;64(12):3936-46. doi: 10.1002/art.37685. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 22933378
-
Associations of limbic-affective brain activity and severity of ongoing chronic arthritis pain are explained by trait anxiety.Neuroimage Clin. 2016 Jul 1;12:269-76. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2016.06.022. eCollection 2016. Neuroimage Clin. 2016. PMID: 27504262 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotransmitter receptor densities are associated with changes in regional Cerebral blood flow during clinical ongoing pain.Hum Brain Mapp. 2022 Dec 1;43(17):5235-5249. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25999. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Hum Brain Mapp. 2022. PMID: 35796178 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoarthritis pain. Recent advances and controversies.Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2018 Jun;12(2):148-153. doi: 10.1097/SPC.0000000000000334. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2018. PMID: 29438127 Review.
-
Brain systems at the intersection of chronic pain and self-regulation.Neurosci Lett. 2019 May 29;702:24-33. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.11.047. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 30503923 Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced anterior cingulate grey matter volume in painful hand osteoarthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2018 Aug;38(8):1429-1435. doi: 10.1007/s00296-018-4085-2. Epub 2018 Jun 23. Rheumatol Int. 2018. PMID: 29936571 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Assessing the Modulatory Effects of tDCS and Acupuncture on Cerebral Blood Flow in Chronic Low Back Pain Using Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion Imaging.Brain Sci. 2025 Feb 28;15(3):261. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15030261. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40149782 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary report: parasympathetic tone links to functional brain networks during the anticipation and experience of visceral pain.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 7;8(1):13410. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31522-2. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30194351 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Preliminary study: quantification of chronic pain from physiological data.Pain Rep. 2022 Oct 4;7(6):e1039. doi: 10.1097/PR9.0000000000001039. eCollection 2022 Nov-Dec. Pain Rep. 2022. PMID: 36213596 Free PMC article.
-
Pain modulatory network is influenced by sex and age in a healthy state and during osteoarthritis progression in rats.Aging Cell. 2021 Feb;20(2):e13292. doi: 10.1111/acel.13292. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Aging Cell. 2021. PMID: 33400367 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alsop, D.C. , Detre, J.A. , Golay, X. , Gunther, M. , Hendrikse, J. et al. (2015). Recommended implementation of arterial spin‐labeled perfusion MRI for clinical applications: A consensus of the ISMRM perfusion study group and the European consortium for ASL in dementia. Magn Reson Med 73, 102–116. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Altman, R. , Alarcon, G. , Appelrouth, D. , Bloch, D. , Borenstein, D. et al. (1990). The American College of Rheumatology criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis of the hand. Arthritis Rheum 33, 1601–1610. - PubMed
-
- Apkarian, A.V. (2010). Human brain imaging studies of chronic pain ‐ translational opportunities In Translational Pain Research: From Mouse to Man, (Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; ). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

