Effect of γ-secretase inhibitor on Th17 cell differentiation and function of mouse psoriasis-like skin inflammation
- PMID: 29523162
- PMCID: PMC5845192
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-018-1442-6
Effect of γ-secretase inhibitor on Th17 cell differentiation and function of mouse psoriasis-like skin inflammation
Abstract
Background: Th17 cells and its effective cytokine IL-17A play an important role in the pathogenesis of abnormal immune responses in psoriasis. Notch1 signaling has been implicated in Th17 cell differentiation and function. In this study, our aim was to evaluate the possible inhibitory effect of Notch1 signaling inhibitor, γ-secretase inhibitor DAPT, on psoriatic Th17 cell differentiation and function in a mouse model of psoriasis-like skin inflammation.
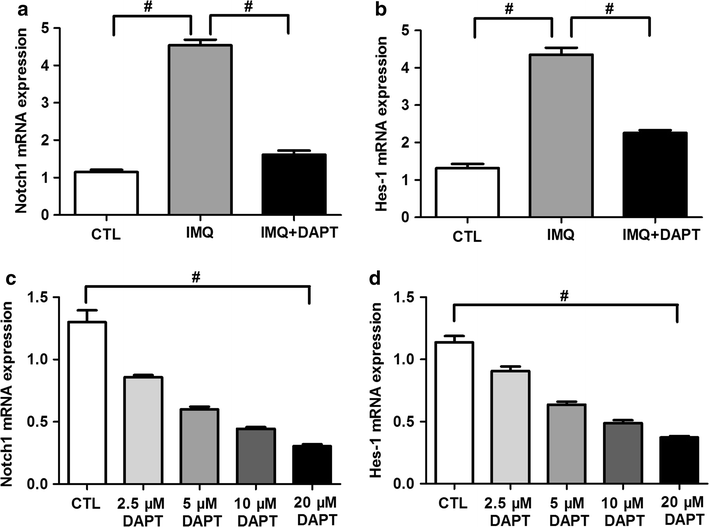
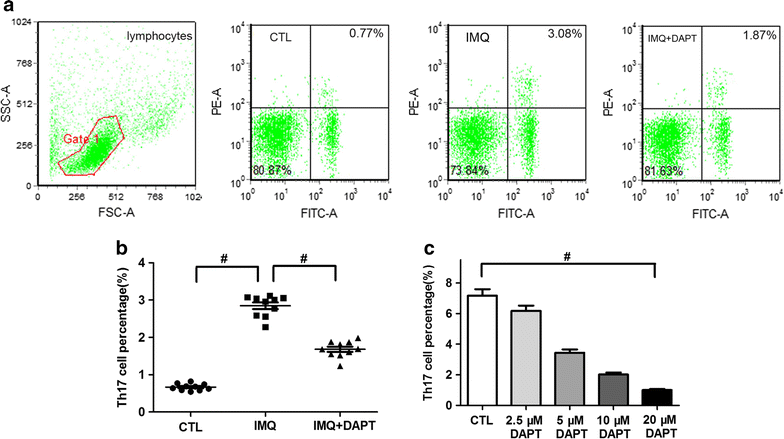
Methods: Mouse psoriasis-like skin inflammation model was established by topical 5% imiquimod (IMQ) application, and experimental mice were divided into control group, IMQ-treated group and IM + DAPT-treated group. DAPT and the equivalent amount of Dimethyl sulfoxide was intraperitoneally injected in IMQ + DAPT-treated group and the other two experimental groups respectively. Skin tissues of the three experimental groups were acquired and stained with haematoxylin and eosin (HE). Splenic single-cells and serum were collected to detect the percentage of Th17 cells, the mRNA expression levels of Notch1 and its target gene Hes-1, Th17-specific transcription factor RORγt and its effective cytokines IL-17A, as well as IL-17A serum concentration. In addition, splenic CD4+ T cells from IMQ-treated mice were isolated and treated by DAPT to further measure the inhibitory effect of DAPT on the Th17 cell differentiation and IL-17A secretion in vitro.
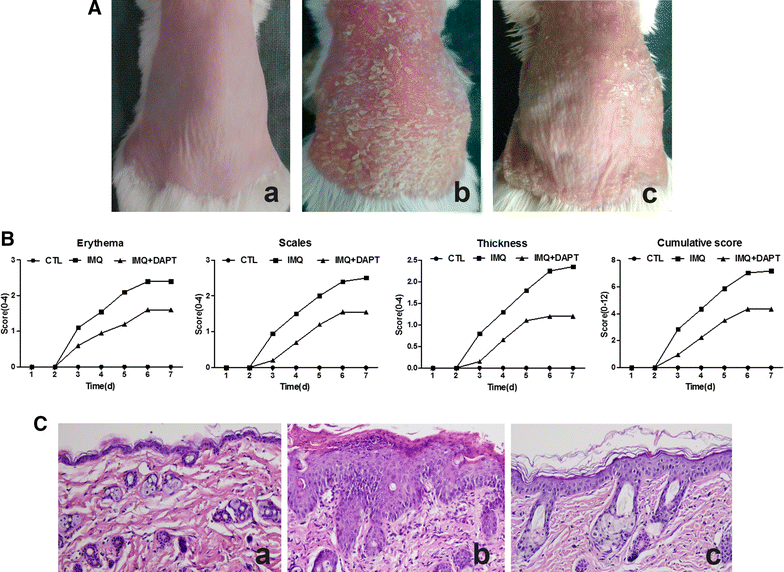
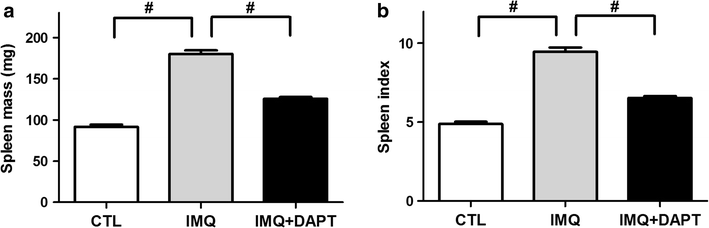
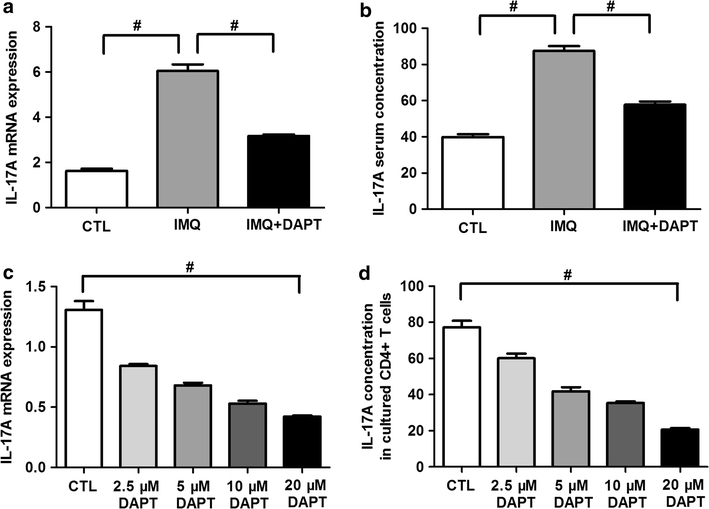
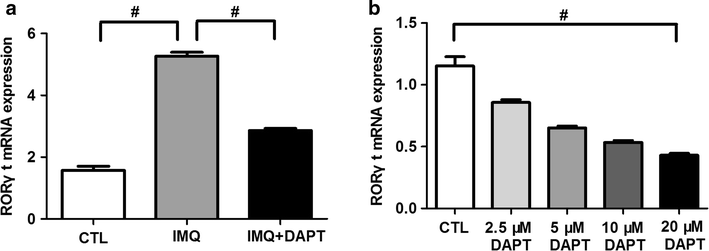
Results: DAPT treatment alleviated the severity of IMQ-induced mouse psoriasis-like skin inflammation and decreased the scores of erythema, scaling and thickening. HE stain reveals obviously reduced epidermal hyperplasia and dermal inflammatory cells infiltration in IMQ + DAPT-treated mice. The increased expression of splenic Th17 cell percentage, along with Notch1, Hes-1, RORγt and IL-17A mRNA and IL-17A serum concentration in IMQ-treated mice were significantly decreased when experimental mice were treated by IMQ and DAPT combinedly. Data obtained from in vitro study in IMQ-treated mice also demonstrated that blocking Notch1 signaling by DAPT can result in a dose-dependent decrease of Th17 cell proportion, mRNA expression of Notch1, Hes-1, RORγt and IL-17A as well as IL-17A secretion in splenic CD4+ T cells.
Conclusion: These data suggest that Notch1 inhibition by DAPT can effectively alleviate the severity of mouse psoriasis-like skin inflammation by regulating the differentiation and function of Th17 cells, indicating that DAPT might be a potential therapeutic candidate for the treatment of psoriatic inflammation.
Keywords: Notch1 signaling; Psoriasis; Th17 cells; γ-secretase inhibitor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Notch1/Hes1‑PTEN/AKT/IL‑17A feedback loop regulates Th17 cell differentiation in mouse psoriasis‑like skin inflammation.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Jul;26(1):223. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12739. Epub 2022 May 18. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 35582997 Free PMC article.
-
Notch-Hes1 Signaling Regulates IL-17A+ γδ +T Cell Expression and IL-17A Secretion of Mouse Psoriasis-Like Skin Inflammation.Mediators Inflamm. 2020 May 12;2020:8297134. doi: 10.1155/2020/8297134. eCollection 2020. Mediators Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 32454795 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased expression of IL-27 in moderate-to-severe psoriasis and its anti-inflammation role in imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like mouse model.J Dermatol Sci. 2017 Feb;85(2):115-123. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2016.11.011. Epub 2016 Nov 28. J Dermatol Sci. 2017. PMID: 27939414
-
Transcription Factor Retinoid-Related Orphan Receptor γt: A Promising Target for the Treatment of Psoriasis.Front Immunol. 2018 May 30;9:1210. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01210. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29899748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Psoriasis: IL-17A and Beyond.Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 2;9:1682. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01682. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30127781 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LY294002 ameliorates psoriatic skin inflammation in mice via blocking the Notch1/Hes1-PTEN/AKT/IL-17A feedback loop.Clin Exp Immunol. 2023 Jul 5;213(1):114-124. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxad025. Clin Exp Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36840628 Free PMC article.
-
Rotenone Treatment Reveals a Role for Electron Transport Complex I in the Subcellular Localization of Key Transcriptional Regulators During T Helper Cell Differentiation.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 7;9:1284. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01284. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29930555 Free PMC article.
-
Notch1/Hes1‑PTEN/AKT/IL‑17A feedback loop regulates Th17 cell differentiation in mouse psoriasis‑like skin inflammation.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Jul;26(1):223. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12739. Epub 2022 May 18. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 35582997 Free PMC article.
-
Notch-Hes1 Signaling Regulates IL-17A+ γδ +T Cell Expression and IL-17A Secretion of Mouse Psoriasis-Like Skin Inflammation.Mediators Inflamm. 2020 May 12;2020:8297134. doi: 10.1155/2020/8297134. eCollection 2020. Mediators Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 32454795 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic Role of Notch Signaling in Human Skin Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 13;21(12):4214. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124214. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32545758 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

