In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a single chain antibody fragment generated in planta with potent rabies neutralisation activity
- PMID: 29523449
- PMCID: PMC6677913
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.02.057
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a single chain antibody fragment generated in planta with potent rabies neutralisation activity
Abstract
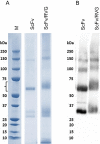
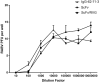
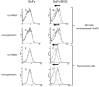
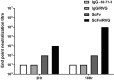
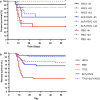
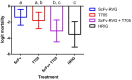
Rabies causes more than 60,000 human deaths annually in areas where the virus is endemic. Importantly, rabies is one of the few pathogens for which there is no treatment following the onset of clinical disease with the outcome of infection being death in almost 100% of cases. Whilst vaccination, and the combination of vaccine and rabies immunoglobulin treatment for post-exposure administration are available, no tools have been identified that can reduce or prevent rabies virus replication once clinical disease has initiated. The search for effective antiviral molecules to treat those that have already developed clinical disease associated with rabies virus infection is considered one of the most important goals in rabies research. The current study assesses a single chain antibody molecule (ScFv) based on a monoclonal antibody that potently neutralises rabies in vitro as a potential therapeutic candidate. The recombinant ScFv was generated in Nicotiana benthamiana by transient expression, and was chemically conjugated (ScFv/RVG) to a 29 amino acid peptide, specific for nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAchR) binding in the CNS. This conjugated molecule was able to bind nAchR in vitro and enter neuronal cells more efficiently than ScFv. The ability of the ScFv/RVG to neutralise virus in vivo was assessed using a staggered administration where the molecule was inoculated either four hours before, two days after or four days after infection. The ScFv/RVG conjugate was evaluated in direct comparison with HRIG and a potential antiviral molecule, Favipiravir (also known as T-705) to indicate whether there was greater bioavailability of the ScFv in the brains of treated mice. The study indicated that the approach taken with the ScFv/RVG conjugate may have utility in the design and implementation of novel tools targetting rabies virus infection in the brain.
Keywords: Blood brain barrier (BBB); Clinical disease; Immunoglobulin; N-acetylcholine receptor; Nicotiana benthamiana; Rabies virus; Single-chain antibody (ScFv).
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
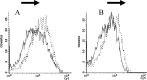
Similar articles
-
Enhanced transport of plant-produced rabies single-chain antibody-RVG peptide fusion protein across an in cellulo blood-brain barrier device.Plant Biotechnol J. 2017 Oct;15(10):1331-1339. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12719. Epub 2017 Apr 19. Plant Biotechnol J. 2017. PMID: 28273388 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering of a recombinant trivalent single-chain variable fragment antibody directed against rabies virus glycoprotein G with improved neutralizing potency.Mol Immunol. 2014 Feb;57(2):66-73. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.08.009. Epub 2013 Oct 1. Mol Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24091293
-
Negative effects of a disulfide bond mismatch in anti-rabies G protein single-chain antibody variable fragment FV57.Mol Immunol. 2014 Jun;59(2):136-41. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2014.01.006. Epub 2014 Mar 2. Mol Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24598312
-
Rabies antibody titers in vaccinees: protection, failure and prospects.Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1992 Mar;30(3):107-12. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1992. PMID: 1506120 Review.
-
Immune reactions against rabies viruses--infection and vaccination.Exp Pathol. 1991;42(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/s0232-1513(11)80028-9. Exp Pathol. 1991. PMID: 1879508 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
An update on antiviral antibody-based biopharmaceuticals.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Sep;86:106760. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106760. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32645633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of Single Chain Variable Fragment (scFv) Molecules in Plants: A Comprehensive Update.Mol Biotechnol. 2020 Mar;62(3):151-167. doi: 10.1007/s12033-020-00241-3. Mol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32036549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combinations of Single Chain Variable Fragments From HIV Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Demonstrate High Potency and Breadth.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 16;12:734110. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.734110. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34603312 Free PMC article.
-
Rabies in a postpandemic world: resilient reservoirs, redoubtable riposte, recurrent roadblocks, and resolute recidivism.Anim Dis. 2023;3(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s44149-023-00078-8. Epub 2023 May 19. Anim Dis. 2023. PMID: 37252063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in nanomedicines for the detection and treatment of diabetic kidney disease.Biomater Biosyst. 2022 Mar 29;6:100047. doi: 10.1016/j.bbiosy.2022.100047. eCollection 2022 Jun. Biomater Biosyst. 2022. PMID: 36824160 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dietzgen RG, et al., Family rhabdoviridae. In: King AMQ, et al., editors. Virus taxonomy: ninth report of the international committee on taxonomy of viruses. 2011 Elsevier Academic Press. p. 686–714.
-
- Schnell M.J. The cell biology of rabies virus: using stealth to reach the brain. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010;8(1):51–61. - PubMed
-
- WHO, WHO Expert Consultation on Rabies, in World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser WHO, Editor. 2013. p. 1–139. - PubMed
-
- Both L. Passive immunity in the prevention of rabies. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12(5):397–407. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

