In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a single chain antibody fragment generated in planta with potent rabies neutralisation activity
- PMID: 29523449
- PMCID: PMC6677913
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.02.057
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a single chain antibody fragment generated in planta with potent rabies neutralisation activity
Abstract
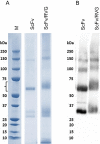
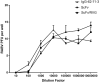
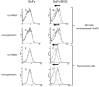
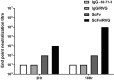
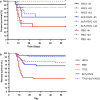
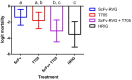
Rabies causes more than 60,000 human deaths annually in areas where the virus is endemic. Importantly, rabies is one of the few pathogens for which there is no treatment following the onset of clinical disease with the outcome of infection being death in almost 100% of cases. Whilst vaccination, and the combination of vaccine and rabies immunoglobulin treatment for post-exposure administration are available, no tools have been identified that can reduce or prevent rabies virus replication once clinical disease has initiated. The search for effective antiviral molecules to treat those that have already developed clinical disease associated with rabies virus infection is considered one of the most important goals in rabies research. The current study assesses a single chain antibody molecule (ScFv) based on a monoclonal antibody that potently neutralises rabies in vitro as a potential therapeutic candidate. The recombinant ScFv was generated in Nicotiana benthamiana by transient expression, and was chemically conjugated (ScFv/RVG) to a 29 amino acid peptide, specific for nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAchR) binding in the CNS. This conjugated molecule was able to bind nAchR in vitro and enter neuronal cells more efficiently than ScFv. The ability of the ScFv/RVG to neutralise virus in vivo was assessed using a staggered administration where the molecule was inoculated either four hours before, two days after or four days after infection. The ScFv/RVG conjugate was evaluated in direct comparison with HRIG and a potential antiviral molecule, Favipiravir (also known as T-705) to indicate whether there was greater bioavailability of the ScFv in the brains of treated mice. The study indicated that the approach taken with the ScFv/RVG conjugate may have utility in the design and implementation of novel tools targetting rabies virus infection in the brain.
Keywords: Blood brain barrier (BBB); Clinical disease; Immunoglobulin; N-acetylcholine receptor; Nicotiana benthamiana; Rabies virus; Single-chain antibody (ScFv).
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
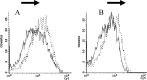
References
-
- Dietzgen RG, et al., Family rhabdoviridae. In: King AMQ, et al., editors. Virus taxonomy: ninth report of the international committee on taxonomy of viruses. 2011 Elsevier Academic Press. p. 686–714.
-
- Schnell M.J. The cell biology of rabies virus: using stealth to reach the brain. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010;8(1):51–61. - PubMed
-
- WHO, WHO Expert Consultation on Rabies, in World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser WHO, Editor. 2013. p. 1–139. - PubMed
-
- Both L. Passive immunity in the prevention of rabies. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12(5):397–407. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

