Evaluation and Management of Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder
- PMID: 29523488
- PMCID: PMC5960024
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esxm.2018.01.004
Evaluation and Management of Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder
Abstract
Introduction: Hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) often has a negative impact on the health and quality of life of women; however, many women do not mention-let alone discuss-this issue with their physicians. Providers of gynecologic services have the opportunity to address this subject with their patients.
Aim: To review the diagnosis and evidence-based treatment of low sexual desire in women with a focus on strategies that can be used efficiently and effectively in the clinic.
Methods: The Medline database was searched for clinically relevant publications on the diagnosis and management of HSDD.
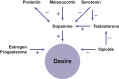
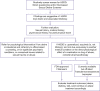
Results: HSDD screening can be accomplished during an office visit with a few brief questions to determine whether further evaluation is warranted. Because women's sexual desire encompasses biological, psychological, social, and contextual components, a biopsychosocial approach to evaluating and treating patients with HSDD is recommended. Although individualized treatment plan development for patients requires independent medical judgment, a simple algorithm can assist in the screening, diagnosis, and management of HSDD. Once a diagnosis of HSDD has been made, interventions can begin with office-based counseling and progress to psychotherapy and/or pharmacotherapy. Flibanserin, a postsynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A agonist and 2A antagonist that decreases serotonin levels and increases dopamine and norepinephrine levels, is indicated for acquired, generalized HSDD in premenopausal women and is the only agent approved in the United States for the treatment of HSDD in women. Other strategies to treat HSDD include using medications indicated for other conditions (eg, transdermal testosterone, bupropion). Bremelanotide, a melanocortin receptor agonist, is in late-stage clinical development.
Conclusions: Providers of gynecologic care are uniquely positioned to screen, counsel, and refer patients with HSDD. Options for pharmacotherapy of HSDD are currently limited to flibanserin, approved by the US Food and Drug Administration, and off-label use of other agents. Clayton AH, Kingsberg SA, Goldstein I. Evaluation and Management of Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder. Sex Med 2018;6:59-74.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Drug Therapies; Flibanserin; Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder; Screening; Sexual Dysfunction.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC: 2000. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4th ed, text rev.
-
- 2017 ICD-10-CM diagnosis code F52.0: hypoactive sexual desire disorder. Available at: http://www.icd10data.com/ICD10CM/codes/F01-F99/F50-F59/F52-/F52.0. Published 2017. Accessed December 7, 2017.
-
- Goldstein I., Kim N.N., Clayton A.H. Hypoactive sexual desire disorder: International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health (ISSWSH) expert consensus panel review. Mayo Clin Proc. 2017;92:114–128. - PubMed
-
- Parish S., Hahn S.R. Hypoactive sexual desire disorder: a review of epidemiology, biopsychology, diagnosis, and treatment. Sex Med Rev. 2016;4:103–120. - PubMed
-
- Shifren J.L., Monz B.U., Russo P.A. Sexual problems and distress in United States women: prevalence and correlates. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;112:970–978. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources