The pseudogene-derived long non-coding RNA SFTA1P suppresses cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in gastric cancer
- PMID: 29523596
- PMCID: PMC5968191
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20171193
The pseudogene-derived long non-coding RNA SFTA1P suppresses cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in gastric cancer
Abstract
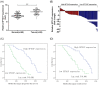
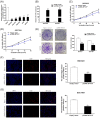
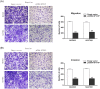
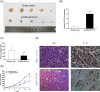
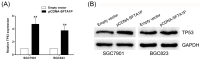
Pseudogenes were once regarded as transcriptionally inactive and without specific molecular function. However, current evidence shows that pseudogene-derived long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) may be crucial regulators of human cancer development, including gastric cancer (GC). In the present study, we report that a pseudogene-derived lncRNA named surfactant associated 1, pseudogene (SFTA1P), which is 693-nt long, was significantly down-regulated in GC tissues compared with that in the adjacent normal tissues. In addition, decreased SFTA1P expression was strongly correlated with advanced tumor lymph node metastasis (TNM) stage, larger tumor size, lymphatic metastasis, and poor prognosis of patients with GC. Moreover, gain-of-function experiments revealed that the overexpression of SFTA1P inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, thus verifying the tumor inhibitory role of SFTA1P in GC. Furthermore, we investigated the potential action mechanism of SFTA1P. Our results showed that down-regulation of SFTA1P may be associated with decreased TP53 expression. In summary, our work suggests that the pseudogene-derived lncRNA SFTA1P functions as a tumor suppressor in GC and thus may act as a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target of GC.
Keywords: SFTA1P; gastric cancer; lncRNA; pseudogene.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

