90Y-DOTATOC Dosimetry-Based Personalized Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy
- PMID: 29523629
- PMCID: PMC6225542
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.117.202903
90Y-DOTATOC Dosimetry-Based Personalized Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy
Abstract
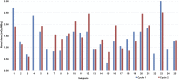
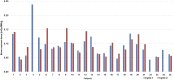
Pretherapy PET with 86Y-DOTATOC is considered the ideal dosimetry protocol for 90Y-DOTATOC therapy; however, its cost, limited availability, and need for infusion of amino acids to mimic the therapy administration limit its use in the clinical setting. The goal of this study was to develop a dosimetric method for 90Y-DOTATOC using 90Y-DOTATOC PET/CT and bremsstrahlung SPECT/CT and to determine whether dosimetry-based administered activities differ significantly from standard administered activities. Methods: This was a prospective phase 2 trial of 90Y-DOTATOC therapy in patients with somatostatin receptor-positive tumors. 90Y-DOTATOC was given in 3 cycles 6-8 wk apart. In the first cycle of therapy, adults received 4.4 GBq and children received 1.85 GBq/m2; the subsequent administered activities were adjusted according to the dosimetry of the preceding cycle so as not to exceed a total kidney dose of 23 Gy and bone marrow dose of 2 Gy. The radiation dose to the kidneys was determined from serial imaging sessions consisting of time-of-flight 90Y-DOTATOC PET/CT at 5 h after therapy and 90Y-DOTATOC bremsstrahlung SPECT/CT at 6, 24, 48, and 72 h. The PET/CT data were used to measure the absolute concentration of 90Y-DOTATOC and to calibrate the bremsstrahlung SPECT kidney clearance data. The radiation dose to the kidneys was determined by multiplying the time-integrated activity (from the fitted biexponential curve of renal clearance of 90Y-DOTATOC) with the energy emitted per decay, divided by the mass of the kidneys. Results: The radiation dose to the kidneys per cycle of 90Y-DOTATOC therapy was highly variable among patients, ranging from 0.32 to 3.0 mGy/MBq. In 17 (85%) of the 20 adult patients who received the second and the third treatment cycles of 90Y-DOTATOC, the administered activity was modified by at least 20% from the starting administered activity. Conclusion: Renal dosimetry of 90Y-DOTATOC is feasible using 90Y-DOTATOC time-of-flight PET/CT and bremsstrahlung SPECT/CT and has a significant impact on the administered activity in treatment cycles.
Keywords: 90Y-DOTATOC; dosimetry; neuroendocrine; peptide receptor radiotherapy; radiobiology/dosimetry; radionuclide therapy.
© 2018 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures


References
-
- Kunikowska J, Krolicki L, Hubalewska-Dydejczyk A, Mikolajczak R, Sowa-Staszczak A, Pawlak D. Clinical results of radionuclide therapy of neuroendocrine tumours with 90Y-DOTATATE and tandem 90Y/177Lu-DOTATATE: which is a better therapy option? Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;38:1788–1797. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vegt E, de Jong M, Wetzels JF, et al. Renal toxicity of radiolabeled peptides and antibody fragments: mechanisms, impact on radionuclide therapy, and strategies for prevention. J Nucl Med. 2010;51:1049–1058. - PubMed
-
- Cybulla M, Weiner SM, Otte A. End-stage renal disease after treatment with 90Y-DOTATOC. Eur J Nucl Med. 2001;28:1552–1554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
