Parathyroidectomy in the Management of Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
- PMID: 29523679
- PMCID: PMC5989682
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.10390917
Parathyroidectomy in the Management of Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
Abstract
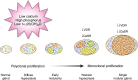
Secondary hyperparathyroidism develops in CKD due to a combination of vitamin D deficiency, hypocalcemia, and hyperphosphatemia, and it exists in nearly all patients at the time of dialysis initiation. There is insufficient data on whether to prefer vitamin D analogs compared with calcimimetics, but the available evidence suggests advantages with combination therapy. Calcium derangements, patient adherence, side effects, and cost limit the use of these agents. When parathyroid hormone level persists >800 pg/ml for >6 months, despite exhaustive medical interventions, monoclonal proliferation with nodular hyperplasia is likely present along with decreased expression of vitamin D and calcium-sensing receptors. Hence, surgical parathyroidectomy should be considered, especially if concomitant disorders exist, such as persistent hypercalcemia or hyperphosphatemia, tissue or vascular calcification including calciphylaxis, and/or worsening osteodystrophy. Parathyroidectomy is associated with 15%-57% greater survival in patients on dialysis, and it also improves hypercalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, tissue calcification, bone mineral density, and health-related quality of life. The parathyroidectomy rate in the United States declined to approximately seven per 1000 dialysis patient-years between 2002 and 2011 despite an increase in average parathyroid hormone levels, reflecting calcimimetics introduction and uncertainty regarding optimal parathyroid hormone targets. Hospitalization rates are 39% higher in the first postoperative year. Hungry bone syndrome occurs in approximately 25% of patients on dialysis, and profound hypocalcemia requires high doses of oral and intravenous calcium along with calcitriol supplementation. Total parathyroidectomy with autotransplantation carries a higher risk of permanent hypocalcemia, whereas risk of hyperparathyroidism recurrence is higher with subtotal parathyroidectomy. Given favorable long-term outcomes from observational parathyroidectomy cohorts, despite surgical risk and postoperative challenges, it is reasonable to consider parathyroidectomy in more patients with medically refractory secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Keywords: Bone Density; CKD-osteodystrophy; Calciphylaxis; Calcitriol; Calcium-Sensing; Humans; Hypercalcemia; Hyperparathyroidism; Hyperplasia; Hypocalcemia; Parathyroidectomy; Receptors; Secondary; Secondary hyperparathyroidism; Uncertainty; Vitamin D; hyperphosphatemia; parathyroidectomy; quality of life; renal dialysis.
Copyright © 2018 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- Levin A, Bakris GL, Molitch M, Smulders M, Tian J, Williams LA, Andress DL: Prevalence of abnormal serum vitamin D, PTH, calcium, and phosphorus in patients with chronic kidney disease: Results of the study to evaluate early kidney disease. Kidney Int 71: 31–38, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Block GA, Klassen PS, Lazarus JM, Ofsthun N, Lowrie EG, Chertow GM: Mineral metabolism, mortality, and morbidity in maintenance hemodialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 15: 2208–2218, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kuwae N, Regidor DL, Kovesdy CP, Kilpatrick RD, Shinaberger CS, McAllister CJ, Budoff MJ, Salusky IB, Kopple JD: Survival predictability of time-varying indicators of bone disease in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 70: 771–780, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Komaba H, Nakamura M, Fukagawa M: Resurgence of parathyroidectomy: Evidence and outcomes. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 26: 243–249, 2017 - PubMed
-
- Tentori F, Wang M, Bieber BA, Karaboyas A, Li Y, Jacobson SH, Andreucci VE, Fukagawa M, Frimat L, Mendelssohn DC, Port FK, Pisoni RL, Robinson BM: Recent changes in therapeutic approaches and association with outcomes among patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism on chronic hemodialysis: The DOPPS study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 10: 98–109, 2015 - PMC - PubMed

