The transcription factor Klf5 is essential for intrahepatic biliary epithelial tissue remodeling after cholestatic liver injury
- PMID: 29523685
- PMCID: PMC5925809
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002372
The transcription factor Klf5 is essential for intrahepatic biliary epithelial tissue remodeling after cholestatic liver injury
Abstract
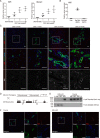
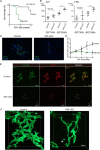
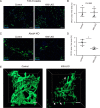
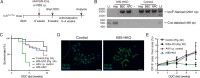
Under various conditions of liver injury, the intrahepatic biliary epithelium undergoes dynamic tissue expansion and remodeling, a process known as ductular reaction. Mouse models defective in inducing such a tissue-remodeling process are more susceptible to liver injury, suggesting a crucial role of this process in liver regeneration. However, the molecular mechanisms regulating the biliary epithelial cell (BEC) dynamics in the ductular reaction remain largely unclear. Here, we demonstrate that the transcription factor Krüppel-like factor 5 (Klf5) is highly enriched in mouse liver BECs and plays a key role in regulating the ductular reaction, specifically under cholestatic injury conditions. Although mice lacking Klf5 in the entire liver epithelium, including both hepatocytes and BECs (Klf5-LKO (liver epithelial-specific knockout) mice), did not exhibit any apparent phenotype in the hepatobiliary system under normal conditions, they exhibited significant defects in biliary epithelial tissue remodeling upon 3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydrocollidine-induced cholangitis, concomitantly with exacerbated cholestasis and reduced survival rate. In contrast, mice lacking Klf5 solely in hepatocytes did not exhibit any such phenotypes, confirming Klf5's specific role in BECs. RNA-sequencing analyses of BECs isolated from the Klf5-LKO mouse livers revealed that the Klf5 deficiency primarily affected expression of cell cycle-related genes. Moreover, immunostaining analysis with the proliferation marker Ki67 disclosed that the Klf5-LKO mice had significantly reduced BEC proliferation levels upon injury. These results indicate that Klf5 plays a critical role in the ductular reaction and biliary epithelial tissue expansion and remodeling by inducing BEC proliferation and thereby contributing to liver regeneration.
Keywords: bile duct; bioinformatics; cell proliferation; ductular reaction (DR); epithelial cell; homeostasis; kruppel-like factor 5 (KLF5); liver injury; regeneration.
© 2018 Okada et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

Similar articles
-
Loss of keratin 19 favours the development of cholestatic liver disease through decreased ductular reaction.J Pathol. 2015 Nov;237(3):343-54. doi: 10.1002/path.4580. Epub 2015 Aug 3. J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26108453
-
Sortilin in Biliary Epithelial Cells Promotes Ductular Reaction and Fibrosis during Cholestatic Injury.Am J Pathol. 2024 Jun;194(6):941-957. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2024.01.023. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Am J Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38493927
-
β-Catenin-NF-κB-CFTR interactions in cholangiocytes regulate inflammation and fibrosis during ductular reaction.Elife. 2021 Oct 5;10:e71310. doi: 10.7554/eLife.71310. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34609282 Free PMC article.
-
Panic at the Bile Duct: How Intrahepatic Cholangiocytes Respond to Stress and Injury.Am J Pathol. 2023 Oct;193(10):1440-1454. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2023.02.012. Epub 2023 Mar 2. Am J Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36870530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ductular hepatocytes.Histol Histopathol. 1995 Apr;10(2):433-56. Histol Histopathol. 1995. PMID: 7599440 Review.
Cited by
-
Specificity Proteins (SP) and Krüppel-like Factors (KLF) in Liver Physiology and Pathology.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 28;24(5):4682. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054682. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative analysis of single-cell RNA-seq and ATAC-seq reveals heterogeneity of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatic organoids.iScience. 2023 Aug 18;26(9):107675. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107675. eCollection 2023 Sep 15. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37680467 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell transcription reveals hepatocyte-to-cholangiocyte reprogramming and biliary gene profile in biliary atresia.Hepatol Commun. 2025 May 6;9(5):e0710. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000710. eCollection 2025 May 1. Hepatol Commun. 2025. PMID: 40366121 Free PMC article.
-
Krüppel-like factor (KLF)5: An emerging foe of cardiovascular health.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022 Feb;163:56-66. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2021.10.002. Epub 2021 Oct 13. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 34653523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of Tgm2 suppresses BMP-mediated hepatocyte-to-cholangiocyte metaplasia in ductular reaction.Cell Prolif. 2024 Oct;57(10):e13646. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13646. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Cell Prolif. 2024. PMID: 38623945 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

