FERTILIZATION-INDEPENDENT SEED-Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 Plays a Dual Role in Regulating Type I MADS-Box Genes in Early Endosperm Development
- PMID: 29523711
- PMCID: PMC5933120
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.17.00534
FERTILIZATION-INDEPENDENT SEED-Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 Plays a Dual Role in Regulating Type I MADS-Box Genes in Early Endosperm Development
Abstract
Early endosperm development presents a unique system in which to uncover epigenetic regulatory mechanisms because the contributing maternal and paternal genomes possess differential epigenetic modifications. In Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), the initiation of endosperm coenocytic growth upon fertilization and the transition to endosperm cellularization are regulated by the FERTILIZATION-INDEPENDENT SEED (FIS)-Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2), a putative H3K27 methyltransferase. Here, we address the possible role of the FIS-PRC2 complex in regulating the type I MADS-box gene family, which has been shown previously to regulate early endosperm development. We show that a subclass of type I MADS-box genes (C2 genes) was expressed in distinct domains of the coenocytic endosperm in wild-type seeds. Furthermore, the C2 genes were mostly up-regulated biallelically during the extended coenocytic phase of endosperm development in the FIS-PRC2 mutant background. Using allele-specific expression analysis, we also identified a small subset of C2 genes subjected to FIS-PRC2-dependent maternal or FIS-PRC2-independent paternal imprinting. Our data support a dual role for the FIS-PRC2 complex in the regulation of C2 type I MADS-box genes, as evidenced by a generalized role in the repression of gene expression at both alleles associated with endosperm cellularization and a specialized role in silencing the maternal allele of imprinted genes.
© 2018 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



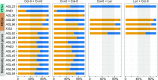
 and
and  (where m denotes maternal transcripts and p denotes paternal transcripts measured by SBE) in both reciprocal crosses, as described previously (Hsieh et al., 2011). P values calculated using Student’s t test are provided in
(where m denotes maternal transcripts and p denotes paternal transcripts measured by SBE) in both reciprocal crosses, as described previously (Hsieh et al., 2011). P values calculated using Student’s t test are provided in 
References
-
- Adams S, Vinkenoog R, Spielman M, Dickinson HG, Scott RJ (2000) Parent-of-origin effects on seed development in Arabidopsis thaliana require DNA methylation. Development 127: 2493–2502 - PubMed
-
- Baud S, Wuillème S, Lemoine R, Kronenberger J, Caboche M, Lepiniec L, Rochat C (2005) The AtSUC5 sucrose transporter specifically expressed in the endosperm is involved in early seed development in Arabidopsis. Plant J 43: 824–836 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

