Rapid nonapeptide synthesis during a critical period of development in the prairie vole: plasticity of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus
- PMID: 29523998
- PMCID: PMC6340296
- DOI: 10.1007/s00429-018-1640-2
Rapid nonapeptide synthesis during a critical period of development in the prairie vole: plasticity of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus
Abstract
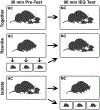
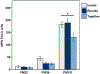
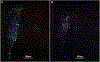
Vasopressin (VP) and oxytocin (OT) are involved in modulating basic physiology and numerous social behaviors. Although the anatomical distributions of nonapeptide neurons throughout development have been described, the functional roles of VP and OT neurons during development are surprisingly understudied, and it is unknown whether they exhibit functional changes throughout early development. We utilized an acute social isolation paradigm to determine if VP and OT neural responses in eight nonapeptide cell groups differ at three different stages of early development in prairie voles. We tested pups at ages that are representative of the three rapid growth stages of the developing brain: postnatal day (PND)2 (closed eyes; poor locomotion), PND9 (eye opening; locomotion; peak brain growth spurt), and PND21 (weaning). Neural responses were examined in pups that (1) were under normal family conditions with their parents and siblings, (2) were isolated from their parents and siblings and then reunited, and (3) were isolated from their parents and siblings. We found that VP and OT neural activity (as assessed via Fos co-localization) did not differ in response to social condition across development. However, remarkably rapid VP and OT synthesis in response to social isolation was observed only in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN) and only in PND9 pups. These results suggest that PVN nonapeptide neurons exhibit distinct cellular properties during a critical period of development, allowing nonapeptide neurons to rapidly upregulate peptide production in response to stressors on a much shorter timescale than has been observed in adult animals.
Keywords: Critical period; Development; Oxytocin; PVN; Prairie vole; Vasopressin.
Figures
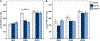
Similar articles
-
Support for the parental practice hypothesis: Subadult prairie voles exhibit similar behavioral and neural profiles when alloparenting kin and non-kin.Behav Brain Res. 2022 Jan 24;417:113571. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113571. Epub 2021 Sep 6. Behav Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 34499932 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol Consumption Decreases Oxytocin Neurons in the Anterior Paraventricular Nucleus of the Hypothalamus in Prairie Voles.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2017 Aug;41(8):1444-1451. doi: 10.1111/acer.13430. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2017. PMID: 28617958
-
Blockade of NK3R signaling in the PVN decreases vasopressin and oxytocin release and c-Fos expression in the magnocellular neurons in response to hypotension.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008 Oct;295(4):R1158-67. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.90402.2008. Epub 2008 Jul 23. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18650316 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic Inputs of Neural Afferent Pathways to Vasopressin- and Oxytocin-Secreting Neurons of Supraoptic and Paraventricular Hypothalamic Nuclei.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2016;16(4):276-287. doi: 10.2174/1871530317666170104124229. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 28056741 Review.
-
Vasopressin and oxytocin receptor systems in the brain: Sex differences and sex-specific regulation of social behavior.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2016 Jan;40:1-23. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2015.04.003. Epub 2015 May 4. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2016. PMID: 25951955 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial: What's Love Got to Do With It: The Evolution of Monogamy.Front Ecol Evol. 2020 Apr;8:110. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2020.00110. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Front Ecol Evol. 2020. PMID: 32782899 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Leveraging the unique social organization of California mice to study circuit-specific effects of oxytocin on behavior.Horm Behav. 2024 Apr;160:105487. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2024.105487. Epub 2024 Jan 27. Horm Behav. 2024. PMID: 38281444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Support for the parental practice hypothesis: Subadult prairie voles exhibit similar behavioral and neural profiles when alloparenting kin and non-kin.Behav Brain Res. 2022 Jan 24;417:113571. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113571. Epub 2021 Sep 6. Behav Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 34499932 Free PMC article.
-
Age-specific and context-specific responses of the medial extended amygdala in the developing prairie vole.Dev Neurobiol. 2018 Dec;78(12):1231-1245. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22648. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Dev Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 30354021 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of Vasopressin and Oxytocin Neurons in the Basal Forebrain and Midbrain of Spiny Mice (Acomys cahirinus).Neuroscience. 2021 Aug 1;468:16-28. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2021.05.034. Epub 2021 Jun 5. Neuroscience. 2021. PMID: 34102266 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bamshad M, Novak MA, de Vries GJ (1994) Cohabitation alters vasopressin innervation and paternal behavior in prairie voles (Microtus ochrogaster). Physiol Behav 56(4):751–758 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

