Cryotherapy and Radiofrequency Ablation for Eradication of Barrett's Esophagus with Dysplasia or Intramucosal Cancer
- PMID: 29524114
- PMCID: PMC7053567
- DOI: 10.1007/s10620-018-5009-4
Cryotherapy and Radiofrequency Ablation for Eradication of Barrett's Esophagus with Dysplasia or Intramucosal Cancer
Abstract
Background and aims: Endoscopic ablation therapy has become the mainstay of treatment of Barrett's associated dysplasia and intramucosal cancer (IMC). The widely available techniques for ablation are radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and cryotherapy. Our aim was to compare eradication rates of metaplasia and dysplasia with both these modalities.
Patients and methods: Retrospective review of prospectively collected database of patients who underwent endoscopic therapy for Barrett's dysplasia or IMC from 2006 to 2011 was performed. Demographic features, comorbidities, and endoscopic data including length of Barrett's segment, hiatal hernia size, interventions during the endoscopy and histological results were reviewed.
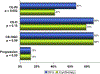
Results: Among 154 patients included, 73 patients were in the RFA and 81 patients were in the cryotherapy group. There was complete eradication of intestinal metaplasia (CE-IM) in 81 (52.6%), complete eradication of dysplasia (CE-D) in 133 (86.4%), and persistent dysplasia or cancer in 19 patients (12.3%). Compared to RFA, cryotherapy patients were found to be older and less likely to have undergone endoscopic mucosal resection. On multivariate analysis, patients who underwent RFA had a threefold higher odds of having CE-IM than those who underwent cryotherapy (odds ratio [OR] 2.9, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.4-6.0, p = 0.004), but CE-D were similar between the two groups (OR 1.7, 95% CI 0.66-4.3, p = 0.28).
Conclusions: Endoscopic therapy is highly effective in eradication of Barrett's associated neoplasia. Patients who underwent cryotherapy were equally likely to achieve CE-D but not CE-IM than patients who underwent RFA. Patient characteristics and preferences may effect choice of treatment selection and outcomes.
Keywords: Ablation; Barrett’s esophagus; Cryotherapy; Dysplasia; Endoscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of Cryotherapy as a Primary Endoscopic Ablation Modality for Dysplastic Barrett's Esophagus and Early Esophageal Neoplasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancer Control. 2020 Jan-Dec;27(1):1073274820976668. doi: 10.1177/1073274820976668. Cancer Control. 2020. PMID: 33297725 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid nitrogen spray cryotherapy-based multimodal endoscopic management of dysplastic Barrett's esophagus and early esophageal neoplasia: retrospective review and long-term follow-up at an academic tertiary care referral center.Dis Esophagus. 2020 Apr 15;33(4):doz095. doi: 10.1093/dote/doz095. Dis Esophagus. 2020. PMID: 31909783 Free PMC article.
-
Salvage cryotherapy after failed radiofrequency ablation for Barrett's esophagus-related dysplasia is safe and effective.Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Sep;82(3):443-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2015.01.033. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015. PMID: 25887715
-
Feasibility of liquid nitrogen cryotherapy after failed radiofrequency ablation for Barrett's esophagus.Dig Endosc. 2017 Sep;29(6):680-685. doi: 10.1111/den.12869. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Dig Endosc. 2017. PMID: 28303613
-
Efficacy and safety outcomes of multimodal endoscopic eradication therapy in Barrett's esophagus-related neoplasia: a systematic review and pooled analysis.Gastrointest Endosc. 2017 Mar;85(3):482-495.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2016.09.022. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017. PMID: 27670227
Cited by
-
Endoscopic cryotherapy: Indications, techniques, and outcomes involving the gastrointestinal tract.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2022 Jan 16;14(1):17-28. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v14.i1.17. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2022. PMID: 35116096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoscopic foregut surgery and interventions: The future is now. The state-of-the-art and my personal journey.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jan 7;25(1):1-41. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i1.1. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30643356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Cryotherapy as a Primary Endoscopic Ablation Modality for Dysplastic Barrett's Esophagus and Early Esophageal Neoplasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancer Control. 2020 Jan-Dec;27(1):1073274820976668. doi: 10.1177/1073274820976668. Cancer Control. 2020. PMID: 33297725 Free PMC article.
-
Organ and function preservation in gastrointestinal cancer: Current and future perspectives on endoscopic ablation.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jun 16;16(6):282-291. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v16.i6.282. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2024. PMID: 38946859 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of cryotherapy in premalignant and malignant esophageal disease: Preventing, treating, palliating disease and enhancing immunogenicity?World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 May 15;17(5):103746. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.103746. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40487973 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arora Z, Garber A, Thota PN. Risk factors for Barrett’s esophagus. J Dig Dis. 2016;17:215–221. - PubMed
-
- Haidry R, Lovat L, Sharma P. Radiofrequency ablation for Barrett’s dysplasia: past, present and the future? Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2015;17:13. - PubMed
-
- Haidry R, Lovat L. Long-term durability of radiofrequency ablation for Barrett’s-related neoplasia. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2015;31:316–320. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical