The Genomic Landscape and Pharmacogenomic Interactions of Clock Genes in Cancer Chronotherapy
- PMID: 29525205
- PMCID: PMC6056007
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cels.2018.01.013
The Genomic Landscape and Pharmacogenomic Interactions of Clock Genes in Cancer Chronotherapy
Abstract
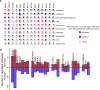
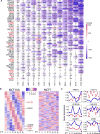
Cancer chronotherapy, treatment at specific times during circadian rhythms, endeavors to optimize anti-tumor effects and to lower toxicity. However, comprehensive characterization of clock genes and their clinical relevance in cancer is lacking. We systematically characterized the alterations of clock genes across 32 cancer types by analyzing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas, Cancer Therapeutics Response Portal, and The Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer databases. Expression alterations of clock genes are associated with key oncogenic pathways, patient survival, tumor stage, and subtype in multiple cancer types. Correlations between expression of clock genes and of other genes in the genome were altered in cancerous versus normal tissues. We identified interactions between clock genes and clinically actionable genes by analyzing co-expression, protein-protein interaction, and chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing data and also found that clock gene expression is correlated to anti-cancer drug sensitivity in cancer cell lines. Our study provides a comprehensive analysis of the circadian clock across different cancer types and highlights potential clinical utility of cancer chronotherapy.
Keywords: cancer; chronotherapy; circadian rhythms; clinical actionable genes; clock genes; drug; pharmacogenomics.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Comment in
-
Escaping Circadian Regulation: An Emerging Hallmark of Cancer?Cell Syst. 2018 Mar 28;6(3):266-267. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2018.03.006. Cell Syst. 2018. PMID: 29596780
References
-
- Akashi M, Okamoto A, Tsuchiya Y, Todo T, Nishida E, Node K. A Positive Role for PERIOD in Mammalian Circadian Gene Expression. Cell Rep. 2014;7:1056–1064. - PubMed
-
- Van Allen EM, Wagle N, Stojanov P, Perrin DL, Cibulskis K, Marlow S, Jane-Valbuena J, Friedrich DC, Kryukov G, Carter SL, et al. Whole-exome sequencing and clinical interpretation of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tumor samples to guide precision cancer medicine. Nat. Med. 2014;20:682–688. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

