Characterization of the immune response elicited by the vaccinia virus L3 protein delivered as naked DNA
- PMID: 29525282
- PMCID: PMC6065253
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.02.033
Characterization of the immune response elicited by the vaccinia virus L3 protein delivered as naked DNA
Abstract
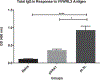
Poxviruses are complex dsDNA viruses with over 200 genes, many of them with unknown role in the stimulation of immune responses. Among these, the vaccinia virus (VACV) L3L ORF encodes an essential protein for the transcription of the VACV early genes. To the best of our knowledge, the immune response elicited by L3 has not been characterized. In this regard, our data describes a DNA L3-coding plasmid (pL3L) that stimulates both, humoral- and cell-mediated immune responses in a mouse model. Cell-mediated immune responses were measured by IFN-γ and IL-4 ELISPOT assays. We performed CD8+ cells depletion and flow cytometry analysis to account for the contribution of cytotoxic T lymphocytes in the IFN-γ production. Moreover, results from ELISPOT were confirmed by measuring the concentration of IL-4 and IFN-γ in supernatant of antigen-stimulated splenocytes by cytokine ELISA. Additionally, dominant antigenic regions of L3 protein were identified by epitope mapping analysis. Humoral immune responses were assessed by ELISA. Specifically, the production of total IgG, IgG1 (TH-2) and IgG2a (TH-1) were determined one week after the final immunization. Our ELISPOT data shows pL3L-immunized animals to produce significantly higher frequencies of IFN-γ Spot-Forming Cells (SFC) versus controls. IL-4 levels remained unchanged in all three groups, demonstrating the increase in antigen-specific IFN-γ releasing cells. Flow cytometry assay results showed that CD8+ T cells are a major contributor to the production of IFN-γ. Moreover, our formulation enhances the production of total IgG, predominantly IgG2a isotype. Immunization with pL3L promotes a robust cytotoxic immune response, crucial against viral pathogens. In addition, our vaccine candidate promotes an increase in IgG levels, especially IgG2a (TH-1 type). Our data encourages further studies of L3 as a novel antigen in vaccine development against poxviruses.
Keywords: Bioterror agents; DNA-vaccine; L3L; Novel antigen; Smallpox; Vaccine.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
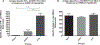
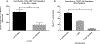
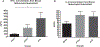

Similar articles
-
Vaccination with a codon-optimized A27L-containing plasmid decreases virus replication and dissemination after vaccinia virus challenge.Vaccine. 2017 Oct 20;35(44):6007-6014. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.05.091. Epub 2017 Jun 16. Vaccine. 2017. PMID: 28629922 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulator-based enhancement of anti smallpox immune responses.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 13;10(4):e0123113. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123113. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25875833 Free PMC article.
-
Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara Can Induce Optimal CD8+ T Cell Responses to Directly Primed Antigens Depending on Vaccine Design.J Virol. 2019 Oct 15;93(21):e01154-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01154-19. Print 2019 Nov 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31375596 Free PMC article.
-
Definition of epitopes and antigens recognized by vaccinia specific immune responses: their conservation in variola virus sequences, and use as a model system to study complex pathogens.Vaccine. 2009 Dec 30;27 Suppl 6(Suppl 6):G21-6. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.10.011. Vaccine. 2009. PMID: 20006135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vaccinia Virus Protein C6: A Multifunctional Interferon Antagonist.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1052:1-7. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-7572-8_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29785476 Review.
Cited by
-
A Synthetic Nanoparticle Based Vaccine Approach Targeting MSP4/5 Is Immunogenic and Induces Moderate Protection Against Murine Blood-Stage Malaria.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 15;10:331. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00331. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30930890 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

