The novel use of botulinum toxin A for the treatment of Raynaud's phenomenon in the toes
- PMID: 29525756
- PMCID: PMC5847911
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2017-219348
The novel use of botulinum toxin A for the treatment of Raynaud's phenomenon in the toes
Abstract
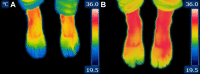
Raynaud's phenomenon is a vasospastic disorder of the digital vessels triggered by exposure to cold or stress. It is most commonly observed in the hands, but also frequently affects the toes. We present three cases of patients with severe Raynaud's phenomenon in the toes, secondary to scleroderma. The diagnosis of Raynaud's syndrome and scleroderma was established according to the 2010 American College of Rheumatology and European League Against Rheumatism criteria. Patients were treated with 10 units of botulinum toxin injected into each foot. Two millilitres was injected into the base of each toe in both the left and right feet. Six weeks postinjection into the toes, patients reported an improvement of cold intolerance, colour change and frequency and severity of Raynaud's attacks. The effects were reported to last up to 5 months. To our knowledge, these are the first reported cases of the treatment of Raynaud's phenomenon in the toes with botulinum toxin A.
Keywords: plastic and reconstructive surgery; rheumatology.
© BMJ Publishing Group Ltd (unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeted high concentration botulinum toxin A injections in patients with Raynaud's phenomenon: a retrospective single-centre experience.Rheumatol Int. 2021 May;41(5):943-949. doi: 10.1007/s00296-020-04606-4. Epub 2020 May 23. Rheumatol Int. 2021. PMID: 32447423
-
[Botulinum toxin type A contribution in the treatment of Raynaud's phenomenon due to systemic sclerosis].Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2013 Dec;58(6):658-62. doi: 10.1016/j.anplas.2011.11.001. Epub 2011 Dec 26. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2013. PMID: 22204894 French.
-
Efficacy of Botulinum Toxin B Injection for Raynaud's Phenomenon and Digital Ulcers in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis.Acta Derm Venereol. 2017 Jul 6;97(7):843-850. doi: 10.2340/00015555-2665. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017. PMID: 28358168 Clinical Trial.
-
Novel Combined Approach for Digital Necrosis Secondary to Raynaud's Phenomenon.Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2021 Oct;55(7):766-771. doi: 10.1177/15385744211005663. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2021. PMID: 33866879 Review.
-
Botulinum toxin A treatment of Raynaud's phenomenon: a review.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Feb;41(4):599-603. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2011.07.006. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 21868066 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Use of Botulinum Neurotoxins in Dermatology: Systematic Review.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Feb 5;13(2):120. doi: 10.3390/toxins13020120. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33562846 Free PMC article.
-
Toxin for Treating Raynaud Conditions in Hands (The TORCH Study): A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024 Jun 14;12(6):e5885. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000005885. eCollection 2024 Jun. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024. PMID: 38881966 Free PMC article.
-
Mobile phone thermography of the toes in patients with systemic sclerosis-a pilot study.Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2024 May 22;8(3):rkae068. doi: 10.1093/rap/rkae068. eCollection 2024. Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2024. PMID: 38855628 Free PMC article.
-
Raynaud's phenomenon.J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2019 Jun;4(2):89-101. doi: 10.1177/2397198319826467. Epub 2019 Feb 13. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2019. PMID: 35382391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Botulinum Toxin Type A in the Treatment of Raynaud's Syndrome: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Mar 31;16(3):e57327. doi: 10.7759/cureus.57327. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38690447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Flavahan NA. Pathophysiological regulation of the cutaneous vascular system in raynaud’s phenomenon. New York: Springer, 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical