miRNAs Targeting ICP4 and Delivered to Susceptible Cells in Exosomes Block HSV-1 Replication in a Dose-Dependent Manner
- PMID: 29526650
- PMCID: PMC6080130
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.02.016
miRNAs Targeting ICP4 and Delivered to Susceptible Cells in Exosomes Block HSV-1 Replication in a Dose-Dependent Manner
Abstract
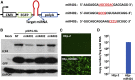
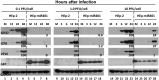
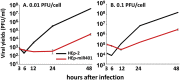
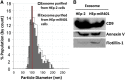
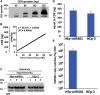
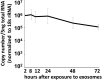
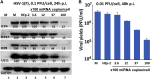
miRNAs are potent tools that in principle can be used to control the replication of infectious agents. The objectives of the studies reported here were to design miRNAs that can block the replication of herpes simplex virus 1 and which could be delivered to infected cells via exosomes. We report the following: (1) We designed three miRNAs targeting the mRNA encoding ICP4, an essential viral regulatory protein. Of the three miRNAs, one miRNA401 effectively blocked ICP4 accumulation and viral replication on transfection into susceptible cells. (2) To facilitate packaging of the miRNA into exosomes, we incorporated into the sequence of miRNA401 an exosome-packaging motif. miRNA401 was shown to be packaged into exosomes and successfully delivered by exosomes to susceptible cells, where it remained stable for at least 72 hr. Finally, the results show that miRNA401 delivered to cells via exosomes effectively reduced virus yields in a miRNA401 dose-dependent fashion. The protocol described in this report can be applied to study viral gene functions without actually deleting or mutagenizing the gene.
Keywords: HSV-1; exosome; target miRNA; viral replication.
Copyright © 2018 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
hnRNPA2B1 Associated with Recruitment of RNA into Exosomes Plays a Key Role in Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Release from Infected Cells.J Virol. 2020 Jun 16;94(13):e00367-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00367-20. Print 2020 Jun 16. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32295924 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations Inactivating Herpes Simplex Virus 1 MicroRNA miR-H2 Do Not Detectably Increase ICP0 Gene Expression in Infected Cultured Cells or Mouse Trigeminal Ganglia.J Virol. 2017 Jan 3;91(2):e02001-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02001-16. Print 2017 Jan 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 27847363 Free PMC article.
-
The HSV-1 Transcription Factor ICP4 Confers Liquid-Like Properties to Viral Replication Compartments.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 24;22(9):4447. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094447. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33923223 Free PMC article.
-
Are miRNAs critical determinants in herpes simplex virus pathogenesis?Microbes Infect. 2018 Oct-Nov;20(9-10):461-465. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2017.12.007. Epub 2017 Dec 26. Microbes Infect. 2018. PMID: 29287990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virus-modified exosomes for targeted RNA delivery; a new approach in nanomedicine.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013 Mar;65(3):348-56. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.07.006. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013. PMID: 22820525 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of host microRNAs in flavivirus-induced neuropathology: An update.J Biosci. 2022;47(3):54. doi: 10.1007/s12038-022-00288-1. J Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36222134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cloaked Viruses and Viral Factors in Cutting Edge Exosome-Based Therapies.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 May 26;8:376. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00376. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32528954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes containing miRNAs targeting HER2 synthesis and engineered to adhere to HER2 on tumor cells surface exhibit enhanced antitumor activity.J Nanobiotechnology. 2020 Oct 27;18(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s12951-020-00711-5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020. PMID: 33109196 Free PMC article.
-
Viruses and neurodegeneration: a growing concern.J Transl Med. 2025 Jan 12;23(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-06025-6. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39800721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Chinese herbal prescription JZ-1 promotes extracellular vesicle production and protects against herpes simplex virus type 2 infection in vitro.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 5;10(5):e27019. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27019. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38495169 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

