Examining the Etiology of Reading Disability as Conceptualized by the Hybrid Model
- PMID: 29527114
- PMCID: PMC5839648
- DOI: 10.1080/10888438.2017.1407321
Examining the Etiology of Reading Disability as Conceptualized by the Hybrid Model
Abstract
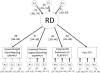
A fairly recent definition of reading disability (RD) is that in the form of a hybrid model. The model views RD as a latent construct that is manifested through various observable unexpected impairments in reading related skills and through inadequate response to intervention. The current report evaluated this new conceptualization of RD from an etiological perspective. The sample consisted of 2737 twin pairs in first through fourth grade (Mage = 8.52) from the Florida Twin Project on Reading. Using twin analyses, results showed that a substantial proportion of genetic variance, a small proportion of shared environmental, and a small proportion of non-shared environmental variance was attributed to the RD factor. Findings suggest that the etiological architecture of RD closely mirrors the structure of the hybrid model of RD.
Keywords: environmental; genetic; hybrid model; reading disability; twins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Longitudinal Associations Among Reading-Related Skills and Reading Comprehension: A Twin Study.Child Dev. 2018 Nov;89(6):e480-e493. doi: 10.1111/cdev.12853. Epub 2017 Jun 1. Child Dev. 2018. PMID: 28569388 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic influence on literacy constructs in kindergarten and first grade: evidence from a diverse twin sample.Behav Genet. 2010 Sep;40(5):591-602. doi: 10.1007/s10519-010-9368-7. Epub 2010 Jun 19. Behav Genet. 2010. PMID: 20563747 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition, Updating Working Memory, and Shifting Predict Reading Disability Symptoms in a Hybrid Model: Project KIDS.Front Psychol. 2018 Mar 20;9:238. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00238. eCollection 2018. Front Psychol. 2018. PMID: 29662458 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-Study Differences in the Etiology of Reading Comprehension: a Meta-Analytical Review of Twin Studies.Behav Genet. 2017 Jan;47(1):52-76. doi: 10.1007/s10519-016-9810-6. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Behav Genet. 2017. PMID: 27630039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding Comorbidity Between Specific Learning Disabilities.New Dir Child Adolesc Dev. 2019 May;2019(165):91-109. doi: 10.1002/cad.20291. Epub 2019 May 9. New Dir Child Adolesc Dev. 2019. PMID: 31070302 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The relation between reading and externalizing behavior: a correlational meta-analysis.Ann Dyslexia. 2024 Jul;74(2):158-186. doi: 10.1007/s11881-024-00307-w. Epub 2024 Jun 29. Ann Dyslexia. 2024. PMID: 38949745 Free PMC article.
-
The Prevalence of Dyslexia: A New Approach to Its Estimation.J Learn Disabil. 2020 Sep/Oct;53(5):354-365. doi: 10.1177/0022219420920377. Epub 2020 May 26. J Learn Disabil. 2020. PMID: 32452713 Free PMC article.
-
Combining Old and New for Better Understanding and Predicting Dyslexia.New Dir Child Adolesc Dev. 2019 May;2019(165):11-23. doi: 10.1002/cad.20289. Epub 2019 Apr 30. New Dir Child Adolesc Dev. 2019. PMID: 31038832 Free PMC article.
-
Reading intervention and neuroplasticity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of brain changes associated with reading intervention.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022 Jan;132:465-494. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.11.011. Epub 2021 Nov 29. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022. PMID: 34856223 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Dyslexia Genetics Research from the Last Two Decades.Brain Sci. 2021 Dec 26;12(1):27. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12010027. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 35053771 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Badian NA. Reading disability defined as a discrepancy between listening and reading comprehension: A longitudinal study of stability, gender differences, and prevalence. Journal of Learning Disabilities. 1999;32:138–148. - PubMed
-
- Bradley R, Danielson L, Hallahan DP. Identification of learning disabilities: Research to practice. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum; 2002.
-
- Burgess SR, Hecht SA, Lonigan CJ. Relations of the home literacy environment to the development of reading-related abilities: A one-year longitudinal study. Reading Research Quarterly. 2002;37:408–426. doi: 10.1598/RRQ.37.4.4. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
