Polysaccharide IV from Lycium barbarum L. Improves Lipid Profiles of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus of Pregnancy by Upregulating ABCA1 and Downregulating Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Transcription 1 via miR-33
- PMID: 29527188
- PMCID: PMC5829030
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00049
Polysaccharide IV from Lycium barbarum L. Improves Lipid Profiles of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus of Pregnancy by Upregulating ABCA1 and Downregulating Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Transcription 1 via miR-33
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Polysaccharide IV from Lycium barbarum L. improves lipid profiles of gestational diabetes mellitus of pregnancy by upregulating ABCA1 and downregulating sterol regulatory element-binding transcription 1 via miR-33.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 6;13:1130062. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1130062. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36686479 Free PMC article.
Abstract
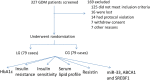
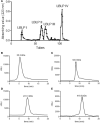
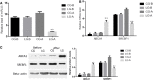
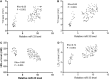
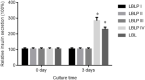
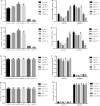
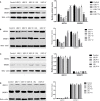
Lycium barbarum L. (LBL) has beneficial effects on gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) but the related mechanism remains unclear. Polysaccharides of LBL (LBLP) are the main bioactive components of LBL. miR-33, ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) and sterol regulatory element-binding transcription 1 (SREBF1) affect lipid profiles, which are associated with GDM risk. LBLP may exert protective against GDM by affecting these molecules. Four LBLP fractions: LBLP-I, LBLP-II, LBLP-III, and LBLP-IV were isolated from LBL and further purified by using DEAE-Sephadex column. The effects of purified each fraction on pancreatic beta cells were comparatively evaluated. A total of 158 GDM patients were recruited and randomly divided into LBL group (LG) and placebo group (CG). miR-33 levels, lipid profiles, insulin resistance and secretory functions were measured. The association between serum miR-33 levels and lipid profiles were evaluated by using Spearman's rank-order correlation test. After 4-week therapy, LBL reduced miR-33 level, insulin resistance and increased insulin secretion of GDM patients. LBL increased the levels of ABCA1, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and reduced miR-33, SREBF1, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), and malondialdehyde. Homeostatic model assessment of β-cell function and insulin resistance was lower in LG than in CG, whereas homeostatic model assessment of β-cell function and insulin secretory function was higher in LG than in CG. There was a strong positive association between miR-33 level and TG, or TC and or LDL-C, and a strong negative association between miR-33 level and HDL-C. The levels of miR-33 had negative relation with ABCA1 and positive relation with SREBF1. ABCA1 has negative relation with TG, TC, and LDL-C and positive relation with HDL-C. Inversely, SREBF1 had positive relation with TG, TC, and LDL-C and negative relation with HDL-C. The main bioactive compound LBLP-IV of LBL increased insulin secretion of beta cells and the levels of ABCA1, and reduced miR-33 levels and SREBF1 in beta cells. However, LBLP-IV could not change the levels of these molecules anymore when miR-33 was overexpressed or silenced. LBLP-IV had the similar effects with LBL on beta cells while other components had no such effects. Thus, LBLP-IV from LBL improves lipid profiles by upregulating ABCA1 and downregulating SREBF1 via miR-33.
Keywords: ATP-binding cassette transporter A1; Lycium barbarum L.; gestational diabetes mellitus; miR-33; sterol regulatory element-binding transcription.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Retraction: Polysaccharide IV from Lycium barbarum L. improves lipid profiles of gestational diabetes mellitus of pregnancy by upregulating ABCA1 and downregulating sterol regulatory element-binding transcription 1 via miR-33.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 6;13:1130062. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1130062. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36686479 Free PMC article.
-
A Common R219K Variant of ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter A1 Gene Alters Atherometabolic Traits in Pregnant Women With Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Dec 17;12:782453. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.782453. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34975757 Free PMC article.
-
The associations between early pregnancy lipid profiles and pregnancy outcomes.J Perinatol. 2017 Feb;37(2):127-133. doi: 10.1038/jp.2016.191. Epub 2016 Oct 27. J Perinatol. 2017. PMID: 27787507
-
Pitavastatin: novel effects on lipid parameters.Atheroscler Suppl. 2011 Nov;12(3):277-84. doi: 10.1016/S1567-5688(11)70887-X. Atheroscler Suppl. 2011. PMID: 22152282 Review.
-
ABCA1 and metabolic syndrome; a review of the ABCA1 role in HDL-VLDL production, insulin-glucose homeostasis, inflammation and obesity.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019 Mar-Apr;13(2):1529-1534. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2019.03.004. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019. PMID: 31336517 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactive Components of Lycium barbarum and Deep-Processing Fermentation Products.Molecules. 2023 Dec 12;28(24):8044. doi: 10.3390/molecules28248044. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38138534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of methylation-driven genes, circulating miRNAs and their potential regulatory mechanisms in gestational diabetes mellitus.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Jan 15;15(1):336-349. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 36777869 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Diabetic Cardiovascular Complications and Related Epigenetic Mechanisms.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jul 19;12:598008. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.598008. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34349728 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Guillen-Sacoto MA, Barquiel B, Hillman N, Burgos MA, Herranz L. Metabolic syndrome and impaired glucose metabolism during early postpartum after twin pregnancies complicated by gestational diabetes mellitus: is the risk comparable to singleton pregnancies? Diabetes Metab (2017) S1262-3636(17):30549–30549.10.1016/j.diabet.2017.10.008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Chi H, Xiao H, Tian X, Wang Y, Yun X, et al. Interleukin 6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), inflammation and metabolism in gestational diabetes mellitus in inner Mongolia. Med Sci Monit (2017) 23:4149–57.10.12659/MSM.903565 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Metzger BE, Coustan DR. Summary and recommendations of the fourth international workshop-conference on gestational diabetes mellitus. The organizing committee. Diabetes Care (1998) 21(Suppl 2):B161–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

