Orbitofrontal sulcogyral morphology is a transdiagnostic indicator of brain dysfunction
- PMID: 29527495
- PMCID: PMC5842758
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2017.12.021
Orbitofrontal sulcogyral morphology is a transdiagnostic indicator of brain dysfunction
Abstract
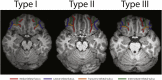
Atypical sulcogyral patterns in the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) are associated with increased risk for schizophrenia, as well as with quantitative traits associated with schizophrenia, such as anhedonia. Here we conduct a cross-diagnostic comparison to assess whether atypical OFC sulcogyral patterns confer risk for multiple brain disorders. We examined structural images from 4 groups of adult participants (N = 189), including those diagnosed with schizophrenia (SZ; N = 49), bipolar disorder (BP; N = 46), attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD; N = 41), and controls (N = 53). OFC sulcogyral pattern types were determined based on the continuity of the medial and lateral orbitofrontal sulcus. Chi-square analysis was performed to compare the sulcogyral pattern frequency distributions between patient groups and controls. We find that both SZ and BP groups had atypical pattern distributions, with increased atypical pattern frequencies relative to controls in the left hemisphere, consistent with the overlapping clinical features and genetic etiology of these disorders (SZ: χ2 = 17.6; p < 0.001; BP: χ2 = 19.2, p < 0.001). The ADHD group distribution did not significantly differ from controls (χ2 = 5.5; p = 0.06, NS.). Similar sulcogyral pattern frequencies across BP and SZ suggest that the sulcogyral phenotype may map more directly to a trait that is transdiagnostic. These results suggest that sulcogyral patterns present a novel morphological indicator for increased susceptibility to multiple psychiatric diagnoses.
Keywords: Attention deficit disorder; Bipolar disorder; Orbitofrontal cortex; Schizophrenia; Sulcogyral pattern.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Orbitofrontal Sulcogyral Pattern as a Transdiagnostic Trait Marker of Early Neurodevelopment in the Social Brain.Clin EEG Neurosci. 2020 Jul;51(4):275-284. doi: 10.1177/1550059420904180. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32028799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sexually dimorphic distribution of orbitofrontal sulcogyral pattern in schizophrenia.Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2011 Aug;65(5):483-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.2011.02229.x. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21851457
-
Orbitofrontal sulcogyral pattern and olfactory sulcus depth in the schizophrenia spectrum.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2016 Feb;266(1):15-23. doi: 10.1007/s00406-015-0587-z. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 25757375
-
Orbitofrontal sulcogyral morphology in patients with cocaine use disorder.Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. 2020 Nov 30;305:111174. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2020.111174. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. 2020. PMID: 32920245 Free PMC article.
-
Prepubertal and early adolescent bipolar I disorder: review of diagnostic validation by Robins and Guze criteria.J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;66 Suppl 7:21-8. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 16124838 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased Heschl's Gyrus Duplication in Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders: A Cross-Sectional MRI Study.J Pers Med. 2021 Jan 12;11(1):40. doi: 10.3390/jpm11010040. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 33445715 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioural profiling of autism connectivity abnormalities.BJPsych Open. 2020 Jan 22;6(1):e11. doi: 10.1192/bjo.2019.102. BJPsych Open. 2020. PMID: 31964452 Free PMC article.
-
Variable Presence of an Evolutionarily New Brain Structure is Related to Trait Impulsivity.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 24:2024.10.23.619912. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.23.619912. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2024 Nov 28:S2451-9022(24)00352-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2024.11.015. PMID: 39484399 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Patterns and predictors of orbitofrontal sulcogyral morphology in a nonclinical population.Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2024 Dec 19;2:imag-2-00389. doi: 10.1162/imag_a_00389. eCollection 2024. Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2024. PMID: 40800483 Free PMC article.
-
Orbitofrontal Sulcogyral Pattern as a Transdiagnostic Trait Marker of Early Neurodevelopment in the Social Brain.Clin EEG Neurosci. 2020 Jul;51(4):275-284. doi: 10.1177/1550059420904180. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32028799 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adler L., Cohen J. Diagnosis and evaluation of adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2004;27:187–201. - PubMed
-
- Andreasen N.C. 1984. Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms (SANS) - PubMed
-
- Andreasen N.C. 1984. Scale for the Assessment of Positive Symptoms.
-
- Armstrong E., Schleicher A., Omran H., Curtis M., Zilles K. The ontogeny of human gyrification. Cereb. Cortex. 1995;1991(5):56–63. - PubMed
-
- Bartholomeusz C.F. Sulcogyral patterns and morphological abnormalities of the orbitofrontal cortex in psychosis. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry. 2013;44:168–177. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

