A novel pooled-sample multiplex luminex assay for high-throughput measurement of relative telomere length
- PMID: 29527774
- PMCID: PMC6105449
- DOI: 10.1002/ajhb.23118
A novel pooled-sample multiplex luminex assay for high-throughput measurement of relative telomere length
Abstract
Objectives: Relative telomere length (RTL) is a potential biomarker of aging and risk for chronic disease. Previously, we developed a probe-based RTL assay on Luminex platform, where probes for Telomere (T) and reference gene (R) for a given DNA sample were tested in a single well. Here, we describe a method of pooling multiple samples in one well to increase the throughput and cost-effectiveness.
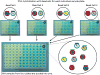
Methods: We used four different microbeads for the same T-probe and four different microbeads for the same R-probe. Each pair of probe sets were hybridized to DNA in separate plates and then pooled in a single plate for all the subsequent steps. We used DNA samples from 60 independent individuals and repeated in multiple batches to test the precision.
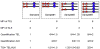
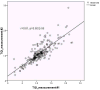
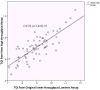
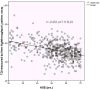
Results: The precision was good to excellent with Intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) of 0.908 (95% CI 0.856-0.942). More than 67% of the variation in the RTL could be explained by sample-to-sample variation; less than 0.1% variation was due to batch-to-batch variation and 0.3% variation was explained by bead-to-bead variation. We increased the throughput of RTL Luminex assay from 60 to 240 samples per run. The new assay was validated against the original Luminex assay without pooling (r = 0.79, P = 1.44 × 10-15 ). In an independent set of samples (n = 550), the new assay showed a negative correlation of RTL with age (r = -0.41), a result providing external validation for the method.
Conclusion: We describe a novel high throughput pooled-sample multiplex Luminex assay for RTL with good to excellent precision suitable for large-scale studies.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Baerlocher GM, Vulto I, de Jong G, Lansdorp PM. Flow cytometry and FISH to measure the average length of telomeres (flow FISH) Nat Protoc. 2006;1(5):2365–2376. - PubMed
-
- Baird DM, Rowson J, Wynford-Thomas D, Kipling D. Extensive allelic variation and ultrashort telomeres in senescent human cells. Nat Genet. 2003;33(2):203–207. - PubMed
-
- Blackburn EH. Structure and function of telomeres. Nature. 1991;350(6319):569–573. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

