Peptide Retention in Hydrophilic Strong Anion Exchange Chromatography Is Driven by Charged and Aromatic Residues
- PMID: 29528219
- PMCID: PMC5937359
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b05157
Peptide Retention in Hydrophilic Strong Anion Exchange Chromatography Is Driven by Charged and Aromatic Residues
Abstract
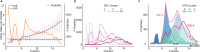
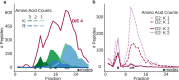
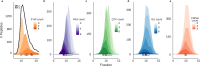
Hydrophilic strong anion exchange chromatography (hSAX) is becoming a popular method for the prefractionation of proteomic samples. However, the use and further development of this approach is affected by the limited understanding of its retention mechanism and the absence of elution time prediction. Using a set of 59 297 confidentially identified peptides, we performed an explorative analysis and built a predictive deep learning model. As expected, charged residues are the major contributors to the retention time through electrostatic interactions. Aspartic acid and glutamic acid have a strong retaining effect and lysine and arginine have a strong repulsion effect. In addition, we also find the involvement of aromatic amino acids. This suggests a substantial contribution of cation-π interactions to the retention mechanism. The deep learning approach was validated using 5-fold cross-validation (CV) yielding a mean prediction accuracy of 70% during CV and 68% on a hold-out validation set. The results of this study emphasize that not only electrostatic interactions but rather diverse types of interactions must be integrated to build a reliable hSAX retention time predictor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anion-exchange chromatography of phosphopeptides: weak anion exchange versus strong anion exchange and anion-exchange chromatography versus electrostatic repulsion-hydrophilic interaction chromatography.Anal Chem. 2015;87(9):4704-11. doi: 10.1021/ac504420c. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Anal Chem. 2015. PMID: 25827581 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence-Specific Model for Peptide Retention Time Prediction in Strong Cation Exchange Chromatography.Anal Chem. 2017 Nov 7;89(21):11795-11802. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b03436. Epub 2017 Oct 17. Anal Chem. 2017. PMID: 28971681
-
Hydrophilic Strong Anion Exchange (hSAX) Chromatography Enables Deep Fractionation of Tissue Proteomes.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1550:69-82. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6747-6_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28188524
-
The binding affinity of uncharged aromatic solutes for negatively charged resins is enhanced by cations via cation-π interactions: The case of sodium ion and arginine.J Chromatogr A. 2019 Jun 21;1595:97-107. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2019.02.043. Epub 2019 Feb 21. J Chromatogr A. 2019. PMID: 30833023
-
Predictions of peptides' retention times in reversed-phase liquid chromatography as a new supportive tool to improve protein identification in proteomics.Proteomics. 2009 Feb;9(4):835-47. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200800544. Proteomics. 2009. PMID: 19160394 Review.
Cited by
-
Spin column-based peptide fractionation alternatives for streamlined tandem mass tag (SL-TMT) sample processing.J Proteomics. 2023 Mar 30;276:104839. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2023.104839. Epub 2023 Feb 8. J Proteomics. 2023. PMID: 36758854 Free PMC article.
-
Retention time prediction using neural networks increases identifications in crosslinking mass spectrometry.Nat Commun. 2021 May 28;12(1):3237. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23441-0. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34050149 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging Parameter Dependencies in High-Field Asymmetric Waveform Ion-Mobility Spectrometry and Size Exclusion Chromatography for Proteome-wide Cross-Linking Mass Spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2022 Mar 22;94(11):4627-4634. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04373. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Anal Chem. 2022. PMID: 35276035 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Proteome Coverage by Using Strong Anion-Exchange in Tandem with Basic-pH Reversed-Phase Chromatography for Sample Multiplexing-Based Proteomics.J Proteome Res. 2024 Aug 2;23(8):2870-2881. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.3c00492. Epub 2023 Nov 14. J Proteome Res. 2024. PMID: 37962907 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

