Performance of U-net based pyramidal lucas-kanade registration on free-breathing multi-b-value diffusion MRI of the kidney
- PMID: 29528241
- PMCID: PMC6223285
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20170813
Performance of U-net based pyramidal lucas-kanade registration on free-breathing multi-b-value diffusion MRI of the kidney
Abstract
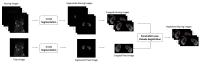
Objective: In free-breathing multi-b-value diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), a series of images typically requires several minutes to collect. During respiration the kidney is routinely displaced and may also undergo deformation. These respiratory motion effects generate artifacts and these are the main sources of error in the quantification of intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) derived parameters. This work proposes a fully automated framework that combines a kidney segmentation to improve the registration accuracy.
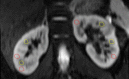
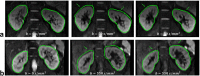
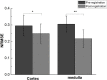
Methods: 10 healthy subjects were recruited to participate in this experiment. For the segmentation, U-net was adopted to acquire the kidney's contour. The segmented kidney then served as a region of interest (ROI) for the registration method, known as pyramidal Lucas-Kanade. Our proposed framework confines the kidney's solution range, thus increasing the pyramidal Lucas-Kanade's accuracy. To demonstrate the feasibility of our presented framework, eight regions of interest were selected in the cortex and medulla, and data stability was estimated by comparing the normalized root-mean-square error (NRMSE) values of the fitted data from the bi-exponential intravoxel incoherent motion model pre- and post- registration.
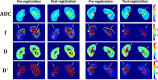
Results: The results show that the NRMSE was significantly lower after registration both in the cortex (p < 0.05) and medulla (p < 0.01) during free-breathing measurements. In addition, expert visual scoring of the derived apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), f, D and D* maps indicated there were significant improvements in the alignment of the kidney in the post-registered image.
Conclusion: The proposed framework can effectively reduce the motion artifacts of misaligned multi-b-value DWIs and the inaccuracies of the ADC, f, D and D* estimations. Advances in knowledge: This study demonstrates the feasibility of our proposed fully automated framework combining U-net based segmentation and pyramidal Lucas-Kanade registration method for improving the alignment of multi-b-value diffusion-weighted MRIs and reducing the inaccuracy of parameter estimation during free-breathing.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) in evaluation of breast lesions: comparison with conventional DWI.Eur J Radiol. 2013 Dec;82(12):e782-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.08.006. Epub 2013 Aug 13. Eur J Radiol. 2013. PMID: 24034833 Clinical Trial.
-
Motion correction of multi-b-value diffusion-weighted imaging in the liver.Acad Radiol. 2012 Dec;19(12):1573-80. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2012.07.005. Epub 2012 Sep 8. Acad Radiol. 2012. PMID: 22963726 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous segmentation and iterative registration method for computing ADC with reduced artifacts from DW-MRI.Med Phys. 2015 May;42(5):2249-60. doi: 10.1118/1.4916799. Med Phys. 2015. PMID: 25979019
-
Stroke assessment with intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI.NMR Biomed. 2016 Mar;29(3):320-8. doi: 10.1002/nbm.3467. Epub 2016 Jan 8. NMR Biomed. 2016. PMID: 26748572
-
Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the liver: effect of triggering methods on regional variability and measurement repeatability of quantitative parameters.Radiology. 2015 Feb;274(2):405-15. doi: 10.1148/radiol.14140759. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Radiology. 2015. PMID: 25232802
Cited by
-
Feature Point Extraction and Motion Tracking of Cardiac Color Ultrasound under Improved Lucas-Kanade Algorithm.J Healthc Eng. 2021 Aug 3;2021:4959727. doi: 10.1155/2021/4959727. eCollection 2021. J Healthc Eng. 2021. PMID: 34394892 Free PMC article.
-
Consensus-based technical recommendations for clinical translation of renal diffusion-weighted MRI.MAGMA. 2020 Feb;33(1):177-195. doi: 10.1007/s10334-019-00790-y. Epub 2019 Nov 1. MAGMA. 2020. PMID: 31676990 Free PMC article.
-
Tri- and bi-exponential diffusion analyses of the kidney: effect of respiratory-controlled acquisition on diffusion parameters.Radiol Phys Technol. 2023 Dec;16(4):478-487. doi: 10.1007/s12194-023-00734-1. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Radiol Phys Technol. 2023. PMID: 37523080
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

