Spatio-temporal dynamics of sulfur bacteria during oxic--anoxic regime shifts in a seasonally stratified lake
- PMID: 29528404
- PMCID: PMC5939864
- DOI: 10.1093/femsec/fiy040
Spatio-temporal dynamics of sulfur bacteria during oxic--anoxic regime shifts in a seasonally stratified lake
Abstract
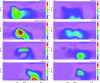
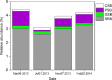
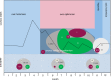
Sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria drive major transformations in the sulfur cycle, and play vital roles in oxic--anoxic transitions in lakes and coastal waters. However, information on the succession of these sulfur bacteria in seasonally stratified lakes using molecular biological techniques is scarce. Here, we used 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing to study the spatio-temporal dynamics of sulfur bacteria during oxic--anoxic regime shifts in Lake Vechten. Oxygen and sulfate were mixed throughout the water column in winter and early spring. Meanwhile, SRB, green sulfur bacteria (GSB), purple sulfur bacteria (PSB), and colorless sulfur bacteria (CSB) exclusively inhabited the sediment. After the water column stratified, oxygen and nitrate concentrations decreased in the hypolimnion and various SRB species expanded into the anoxic hypolimnion. Consequently, sulfate was reduced to sulfide, stimulating the growth of PSB and GSB in the metalimnion and hypolimnion during summer stratification. When hypoxia spread throughout the water column during fall turnover, SRB and GSB vanished from the water column, whereas CSB (mainly Arcobacter) and PSB (Lamprocystis) became dominant and oxidized the accumulated sulfide under micro-aerobic conditions. Our results support the view that, once ecosystems have become anoxic and sulfidic, a large oxygen influx is needed to overcome the anaerobic sulfur cycle and bring the ecosystems back into their oxic state.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Succession of Bacterial Communities in a Seasonally Stratified Lake with an Anoxic and Sulfidic Hypolimnion.Front Microbiol. 2017 Dec 14;8:2511. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02511. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29312212 Free PMC article.
-
Oxic-anoxic regime shifts mediated by feedbacks between biogeochemical processes and microbial community dynamics.Nat Commun. 2017 Oct 6;8(1):789. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00912-x. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28986518 Free PMC article.
-
Succession of bacteria and archaea involved in the nitrogen cycle of a seasonally stratified lake.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2023 Jan 17;370:fnad013. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnad013. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2023. PMID: 36796795 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfur metabolism in phototrophic sulfur bacteria.Adv Microb Physiol. 2009;54:103-200. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2911(08)00002-7. Adv Microb Physiol. 2009. PMID: 18929068 Review.
-
Molecular Physiology of Anaerobic Phototrophic Purple and Green Sulfur Bacteria.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 15;22(12):6398. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126398. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34203823 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of Intracellular Elemental Sulfur Oxidation in Beggiatoa leptomitoformis, Where Persulfide Dioxygenase Plays a Key Role.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 11;25(20):10962. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010962. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456744 Free PMC article.
-
Global diversity and inferred ecophysiology of microorganisms with the potential for dissimilatory sulfate/sulfite reduction.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2023 Sep 5;47(5):fuad058. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuad058. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37796897 Free PMC article.
-
Physically stable yet biologically sensitive: multiyear ecological dynamics of anoxygenic phototrophs in stably redox-stratified Lake Cadagno.Aquat Sci. 2025;87(2):58. doi: 10.1007/s00027-025-01183-1. Epub 2025 Apr 16. Aquat Sci. 2025. PMID: 40255984 Free PMC article.
-
Host population diversity as a driver of viral infection cycle in wild populations of green sulfur bacteria with long standing virus-host interactions.ISME J. 2021 Jun;15(6):1569-1584. doi: 10.1038/s41396-020-00870-1. Epub 2021 Jan 15. ISME J. 2021. PMID: 33452481 Free PMC article.
-
Fairy circles reveal the resilience of self-organized salt marshes.Sci Adv. 2021 Feb 5;7(6):eabe1100. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abe1100. Print 2021 Feb. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 33547078 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biderre-Petit C, Boucher D, Kuever J et al. . Identification of sulfur-cycle prokaryotes in a low-sulfate lake (Lake Pavin) using aprA and 16S rRNA gene markers. Microb Ecol. 2011;61:313–27. - PubMed
-
- Biebl H, Pfennig N. Growth yields of green sulfur bacteria in mixed cultures with sulfur and sulfate reducing bacteria. Arch Microbiol. 1978;117:9–16.
-
- Bokulich NA, Rideout JR, Kopylova E et al. . A standardized, entensible framework for optimizing classification improves marker-gene taxonomic assignments. Peer J PrePrints. 2015;3:e934v2.
-
- Breitburg D, Levin LA, Oschlies A et al. . Declining oxygen in the global ocean and coastal waters. Science. 2018;359:eaam7240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

