Regio- and Stereospecific Synthesis of Oridonin D-Ring Aziridinated Analogues for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer via Mediated Irreversible Covalent Warheads
- PMID: 29528645
- PMCID: PMC6388690
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01514
Regio- and Stereospecific Synthesis of Oridonin D-Ring Aziridinated Analogues for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer via Mediated Irreversible Covalent Warheads
Abstract
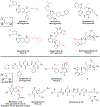
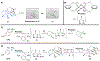
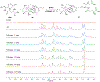
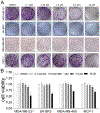
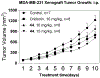
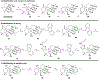
Covalent drug discovery has undergone a resurgence in recent years due to comprehensive optimization of the structure-activity relationship (SAR) and the structure-reactivity relationship (SRR) for covalent drug candidates. The natural product oridonin maintains an impressive pharmacological profile through its covalent enone warhead on the D-ring and has attracted substantial SAR studies to characterize its potential in the development of new molecular entities for the treatment of various human cancers and inflammation. Herein, for the first time, we report the excessive reactivity of this covalent warhead and mediation of the covalent binding capability through a Rh2(esp)2-catalyzed mild and concise regio- and stereospecific aziridination approach. Importantly, aziridonin 44 (YD0514), with a more-druglike irreversible covalent warhead, has been identified to significantly induce apoptosis and inhibit colony formation against triple-negative breast cancer with enhanced antitumor effects in vitro and in vivo while displaying lower toxicity to normal human mammary epithelial cells in comparison to oridonin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


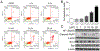
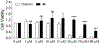
References
-
- Singh J; Petter RC; Baillie TA; Whitty A The resurgence of covalent drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2011, 10, 307–317. - PubMed
-
- Barf T; Kaptein A Irreversible protein kinase inhibitors: balancing the benefits and risks. J. Med. Chem 2012, 55, 6243–6262. - PubMed
-
- Finlay MR; Anderton M; Ashton S; Ballard P; Bethel PA; Box MR; Bradbury RH; Brown SJ; Butterworth S; Campbell A; Chorley C; Colclough N; Cross DA; Currie GS; Grist M; Hassall L; Hill GB; James D; James M; Kemmitt P; Klinowska T; Lamont G; Lamont SG; Martin N; McFarland HL; Mellor MJ; Orme JP; Perkins D; Perkins P; Richmond G; Smith P; Ward RA; Waring MJ; Whittaker D; Wells S; Wrigley GL Discovery of a potent and selective EGFR inhibitor (AZD9291) of both sensitizing and T790M resistance mutations that spares the wild type form of the receptor. J.Med. Chem 2014, 57, 8249–8267. - PubMed
-
- Engel J; Richters A; Getlik M; Tomassi S; Keul M; Termathe M; Lategahn J; Becker C; Mayer-Wrangowski S; Grutter C; Uhlenbrock N; Krull J; Schaumann N; Eppmann S; Kibies P; Hoffgaard F; Heil J; Menninger S; Ortiz-Cuaran S; Heuckmann JM; Tinnefeld V; Zahedi RP; Sos ML; Schultz-Fademrecht C; Thomas RK; Kast SM; Rauh D Targeting drug resistance in EGFR with covalent inhibitors: a structure-based design approach. J. Med. Chem 2015, 58, 6844–6863. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

