Large-scale profiling of noncoding RNA function in yeast
- PMID: 29529031
- PMCID: PMC5864082
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007253
Large-scale profiling of noncoding RNA function in yeast
Abstract
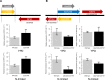
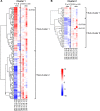
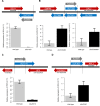
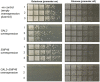
Noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) are emerging as key regulators of cellular function. We have exploited the recently developed barcoded ncRNA gene deletion strain collections in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae to investigate the numerous ncRNAs in yeast with no known function. The ncRNA deletion collection contains deletions of tRNAs, snoRNAs, snRNAs, stable unannotated transcripts (SUTs), cryptic unstable transcripts (CUTs) and other annotated ncRNAs encompassing 532 different individual ncRNA deletions. We have profiled the fitness of the diploid heterozygous ncRNA deletion strain collection in six conditions using batch and continuous liquid culture, as well as the haploid ncRNA deletion strain collections arrayed individually onto solid rich media. These analyses revealed many novel environmental-specific haplo-insufficient and haplo-proficient phenotypes providing key information on the importance of each specific ncRNA in every condition. Co-fitness analysis using fitness data from the heterozygous ncRNA deletion strain collection identified two ncRNA groups required for growth during heat stress and nutrient deprivation. The extensive fitness data for each ncRNA deletion strain has been compiled into an easy to navigate database called Yeast ncRNA Analysis (YNCA). By expanding the original ncRNA deletion strain collection we identified four novel essential ncRNAs; SUT527, SUT075, SUT367 and SUT259/691. We defined the effects of each new essential ncRNA on adjacent gene expression in the heterozygote background identifying both repression and induction of nearby genes. Additionally, we discovered a function for SUT527 in the expression, 3' end formation and localization of SEC4, an essential protein coding mRNA. Finally, using plasmid complementation we rescued the SUT075 lethal phenotype revealing that this ncRNA acts in trans. Overall, our findings provide important new insights into the function of ncRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Turowski TW, Tollervey D (2015) Cotranscriptional events in eukaryotic ribosome synthesis. WIREs-RNA 6: 129–139. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1263 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Massenet S, Bertrand E, Verheggen C (2017) Assembly and trafficking of box C/D and H/ACA snoRNPs. RNA Biol 14: 680–692. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1243646 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Papasaikas P, Valcarcel J (2016) The Spliceosome: The Ultimate RNA Chaperone and Sculptor. Trends Biochem Sci 41: 386–386. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.12.010 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Djebali S, Davis CA, Merkel A, Dobin A, Lassmann T, et al. (2012) Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 489: 101–108. doi: 10.1038/nature11233 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

