Protease signaling through protease activated receptor 1 mediate nerve activation by mucosal supernatants from irritable bowel syndrome but not from ulcerative colitis patients
- PMID: 29529042
- PMCID: PMC5846775
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193943
Protease signaling through protease activated receptor 1 mediate nerve activation by mucosal supernatants from irritable bowel syndrome but not from ulcerative colitis patients
Abstract
Background & aims: The causes of gastrointestinal complaints in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) remain poorly understood. Altered nerve function has emerged as an important pathogenic factor as IBS mucosal biopsy supernatants consistently activate enteric and sensory neurons. We investigated the neurally active molecular components of such supernatants from patients with IBS and quiescent ulcerative colitis (UC).
Method: Effects of supernatants from 7 healthy controls (HC), 20 IBS and 12 UC patients on human and guinea pig submucous neurons were studied with neuroimaging techniques. We identify differentially expressed proteins with proteome analysis.
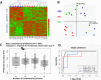
Results: Nerve activation by IBS supernatants was prevented by the protease activated receptor 1 (PAR1) antagonist SCHE79797. UC supernatants also activated enteric neurons through protease dependent mechanisms but without PAR1 involvement. Proteome analysis of the supernatants identified 204 proteins, among them 17 proteases as differentially expressed between IBS, UC and HC. Of those the four proteases elastase 3a, chymotrypsin C, proteasome subunit type beta-2 and an unspecified isoform of complement C3 were significantly more abundant in IBS compared to HC and UC supernatants. Of eight proteases, which were upregulated in IBS, the combination of elastase 3a, cathepsin L and proteasome alpha subunit-4 showed the highest prediction accuracy of 98% to discriminate between IBS and HC groups. Elastase synergistically potentiated the effects of histamine and serotonin-the two other main neuroactive substances in the IBS supernatants. A serine protease inhibitor isolated from the probiotic Bifidobacterium longum NCC2705 (SERPINBL), known to inhibit elastase-like proteases, prevented nerve activation by IBS supernatants.
Conclusion: Proteases in IBS and UC supernatants were responsible for nerve activation. Our data demonstrate that proteases, particularly those signalling through neuronal PAR1, are biomarker candidates for IBS, and protease profiling may be used to characterise IBS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of human enteric neurons by supernatants of colonic biopsy specimens from patients with irritable bowel syndrome.Gastroenterology. 2009 Oct;137(4):1425-34. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.07.005. Epub 2009 Jul 28. Gastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 19596012
-
Submucous rather than myenteric neurons are activated by mucosal biopsy supernatants from irritable bowel syndrome patients.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012 Dec;24(12):1134-e572. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12011. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012. PMID: 22963673
-
Molecular defects in mucosal serotonin content and decreased serotonin reuptake transporter in ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome.Gastroenterology. 2004 Jun;126(7):1657-64. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.03.013. Gastroenterology. 2004. PMID: 15188158
-
Protease activated receptor 2: a new target for IBS treatment.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Aug;12 Suppl 1:95-102. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2008. PMID: 18924448 Review.
-
Enteric P2X receptors as potential targets for drug treatment of the irritable bowel syndrome.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Apr;141(8):1294-302. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705761. Epub 2004 Mar 29. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15051631 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Serpin-positive Bifidobacterium breve CNCM I-5644 improves intestinal permeability in two models of irritable bowel syndrome.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 17;12(1):19776. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21746-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36396717 Free PMC article.
-
Serine protease inhibitors and human wellbeing interplay: new insights for old friends.PeerJ. 2019 Aug 30;7:e7224. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7224. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31531264 Free PMC article.
-
Colonic Gene Expression and Fecal Microbiota in Diarrhea-predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Increased Toll-like Receptor 4 but Minimal Inflammation and no Response to Mesalazine.J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021 Apr 30;27(2):279-291. doi: 10.5056/jnm20205. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021. PMID: 33795545 Free PMC article.
-
Carbohydrate-controlled serine protease inhibitor (serpin) production in Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 31;11(1):7236. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86740-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33790385 Free PMC article.
-
A physiatrist's understanding and application of the current literature on chronic pelvic pain: a narrative review.Pain Rep. 2021 Aug 30;6(3):e949. doi: 10.1097/PR9.0000000000000949. eCollection 2021 Sep-Oct. Pain Rep. 2021. PMID: 34476302 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Enck P, Aziz Q, Barbara G, Farmer AD, Fukudo S, Mayer EA, et al. Irritable bowel syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primer. 2016;2: 16014 doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.14 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nasser Y, Boeckxstaens GE, Wouters MM, Schemann M, Vanner S. Using human intestinal biopsies to study the pathogenesis of irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil Off J Eur Gastrointest Motil Soc. 2014;26: 455–469. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12316 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Buhner S, Li Q, Vignali S, Barbara G, De Giorgio R, Stanghellini V, et al. Activation of human enteric neurons by supernatants of colonic biopsy specimens from patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2009;137: 1425–1434. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.07.005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barbara G, Wang B, Stanghellini V, de Giorgio R, Cremon C, Di Nardo G, et al. Mast cell-dependent excitation of visceral-nociceptive sensory neurons in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2007;132: 26–37. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.11.039 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Buhner S, Braak B, Li Q, Kugler EM, Klooker T, Wouters M, et al. Neuronal activation by mucosal biopsy supernatants from irritable bowel syndrome patients is linked to visceral sensitivity. Exp Physiol. 2014; doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2014.080036 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

