Development of a Rapid Diagnostic Test Kit to Detect IgG/IgM Antibody against Zika Virus Using Monoclonal Antibodies to the Envelope and Non-structural Protein 1 of the Virus
- PMID: 29529852
- PMCID: PMC5858665
- DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2018.56.1.61
Development of a Rapid Diagnostic Test Kit to Detect IgG/IgM Antibody against Zika Virus Using Monoclonal Antibodies to the Envelope and Non-structural Protein 1 of the Virus
Abstract
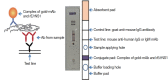
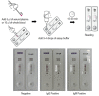
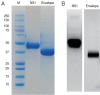
We developed a Rapid Diagnostic Test (RDT) kit for detecting IgG/IgM antibodies against Zika virus (ZIKV) using monoclonal antibodies to the envelope (E) and non-structural protein 1 (NS1) of ZIKV. These proteins were produced using baculovirus expression vector with Sf9 cells. Monoclonal antibodies J2G7 to NS1 and J5E1 to E protein were selected and conjugated with colloidal gold to produce the Zika IgG/IgM RDT kit (Zika RDT). Comparisons with ELISA, plaque reduction neutralization test (PRNT), and PCR were done to investigate the analytical sensitivity of Zika RDT, which resulted in 100% identical results. Sensitivity and specificity of Zika RDT in a field test was determined using positive and negative samples from Brazil and Korea. The diagnostic accuracy of Zika RDT was fairly high; sensitivity and specificity for IgG was 99.0 and 99.3%, respectively, while for IgM it was 96.7 and 98.7%, respectively. Cross reaction with dengue virus was evaluated using anti-Dengue Mixed Titer Performance Panel (PVD201), in which the Zika RDT showed cross-reactions with DENV in 16.7% and 5.6% in IgG and IgM, respectively. Cross reactions were not observed with West Nile, yellow fever, and hepatitis C virus infected sera. Zika RDT kit is very simple to use, rapid to assay, and very sensitive, and highly specific. Therefore, it would serve as a choice of method for point-of-care diagnosis and large scale surveys of ZIKV infection under clinical or field conditions worldwide in endemic areas.
Keywords: NS1; RDT; Zika; cross reaction; diagnostics; envelope; flavivirus; monoclonal antibody.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Serodiagnosis of Zika virus (ZIKV) infections by a novel NS1-based ELISA devoid of cross-reactivity with dengue virus antibodies: a multicohort study of assay performance, 2015 to 2016.Euro Surveill. 2016 Dec 15;21(50):30426. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2016.21.50.30426. Euro Surveill. 2016. PMID: 28006649 Free PMC article.
-
Added value of IgA antibodies against Zika virus non-structural protein 1 in the diagnosis of acute Zika virus infections.J Virol Methods. 2019 May;267:8-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2019.02.005. Epub 2019 Feb 16. J Virol Methods. 2019. PMID: 30779938
-
Re-evaluation of routine dengue virus serology in travelers in the era of Zika virus emergence.J Clin Virol. 2017 Jul;92:25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2017.05.001. Epub 2017 May 3. J Clin Virol. 2017. PMID: 28505571
-
Humoral cross-reactivity between Zika and dengue viruses: implications for protection and pathology.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2017 May 10;6(5):e33. doi: 10.1038/emi.2017.42. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2017. PMID: 28487557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zika Virus Envelope Protein and Antibody Complexes.Subcell Biochem. 2018;88:147-168. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-8456-0_7. Subcell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29900496 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic accuracy of DPP Fever Panel II Asia tests for tropical fever diagnosis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Apr 10;18(4):e0012077. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012077. eCollection 2024 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 38598549 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered NS1 for Sensitive, Specific Zika Virus Diagnosis from Patient Serology.Emerg Infect Dis. 2021 May;27(5):1427-1437. doi: 10.3201/eid2705.190121. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33900180 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Zika virus neutralizing antibodies in normal healthy Thais.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 21;8(1):17193. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35643-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30464242 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Clinical Evaluation of a Rapid Diagnostic Test for Yellow Fever Non-Structural Protein 1.Korean J Parasitol. 2019 Jun;57(3):283-290. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2019.57.3.283. Epub 2019 Jun 30. Korean J Parasitol. 2019. PMID: 31284351 Free PMC article.
-
High correlation between Zika virus NS1 antibodies and neutralizing antibodies in selected serum samples from normal healthy Thais.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 18;9(1):13498. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49569-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31534148 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Dick GW. Zika virus. II. Pathogenicity and physical properties. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1952;46:521–534. - PubMed
-
- Macnamara FN. Zika virus: a report on three cases of human infection during an epidemic of jaundice in Nigeria. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1954;48:139–145. - PubMed
-
- Marchette NJ, Garcia R, Rudnick A. Isolation of Zika virus from Aedes aegypti mosquitoes in Malaysia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1969;18:411–415. - PubMed
-
- Duffy MR, Chen TH, Hancock WT, Powers AM, Kool JL, Lanciotti RS, Pretrick M, Marfel M, Holzbauer S, Dubray C, Guillaumot L, Griggs A, Bel M, Lambert AJ, Laven J, Kosoy O, Panella A, Biggerstaff BJ, Fischer M, Hayes EB. Zika virus outbreak on Yap Island, Federated States of Micronesia. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:2536–2543. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

