Incidence and Risk Factors for Overweight and Obesity after Initiation of Antiretroviral Therapy in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania
- PMID: 29529909
- PMCID: PMC6748468
- DOI: 10.1177/2325958218759759
Incidence and Risk Factors for Overweight and Obesity after Initiation of Antiretroviral Therapy in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania
Abstract
Objective: To describe the incidence of and risk factors for overweight and obesity following antiretroviral therapy (ART) initiation.
Methods: We used Cox proportional hazards models to investigate risk factors for incident overweight and obesity in 79 074 individuals aged 15 years or older who initiated ART in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania.
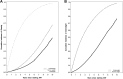
Results: Twenty-five percent of the patients became overweight and 10% became obese. The incidence rate of obesity was 3.2 per 100 person-years (95% confidence interval [CI]: 3.1-3.3) in patients who were of normal weight before starting ART and 22.6 per 100 person-years (95% CI: 21.9-23.3) in those who were overweight. Lower CD4 count was associated with a higher risk of overweight and obesity ( P value for trend < .0001).
Conclusion: There is a high burden of overweight and obesity after starting ART, leading to proportions of these 2 conditions that are similar to those in the general population.
Keywords: antiretroviral therapy; incidence; obesity; overweight; risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS. Global HIV Statistics. 2014. http://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet. Accessed February 9, 2018.
-
- The United Republic of Tanzania. Global AIDS Response Country Progress Report. Dar es Salaam, Tanzania: UNAIDS; 2014.
-
- WHO. Antiretroviral therapy for HIV infection in adults and adolescents. WHO; http://www.who.int/hiv/pub/arv/adult2010/en/. Accessed February 10, 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials