Molecular iodine/doxorubicin neoadjuvant treatment impair invasive capacity and attenuate side effect in canine mammary cancer
- PMID: 29530037
- PMCID: PMC5848438
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-018-1411-6
Molecular iodine/doxorubicin neoadjuvant treatment impair invasive capacity and attenuate side effect in canine mammary cancer
Abstract
Background: Mammary cancer has a high incidence in canines and is an excellent model of spontaneous carcinogenesis. Molecular iodine (I2) exerts antineoplastic effects on different cancer cells activating re-differentiation pathways. In co-administration with anthracyclines, I2 impairs chemoresistance installation and prevents the severity of side effects generated by these antineoplastic drugs. This study is a random and double-blind protocol that analyzes the impact of I2 (10 mg/day) in two administration schemes of Doxorubicin (DOX; 30 mg/m2) in 27 canine patients with cancer of the mammary gland. The standard scheme (sDOX) includes four cycles of DOX administered intravenously for 20 min every 21 days, while the modified scheme (mDOX) consists of more frequent chemotherapy (four cycles every 15 days) with slow infusion (60 min). In both schemes, I2 or placebo (colored water) was supplemented daily throughout the treatment.
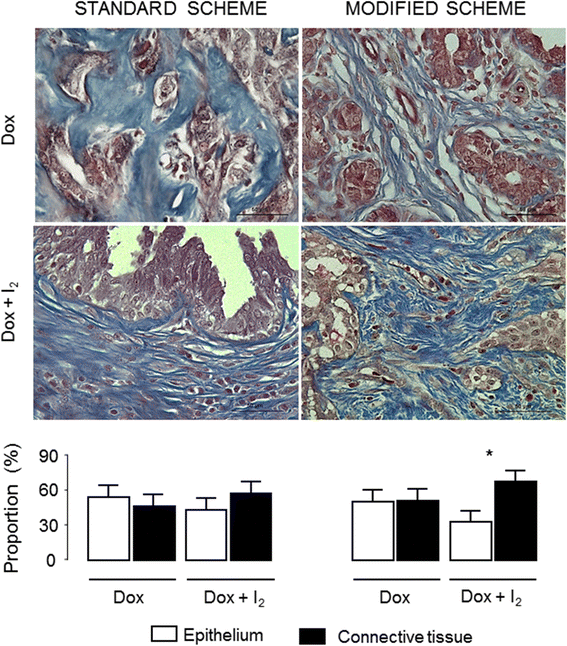
Results: mDOX attenuated the severity of adverse events (VCOG-CTCAE) in comparison with the sDOX group. The overall tumor response rate (RECIST criteria) for all dogs was 18% (interval of reduction 48-125%), and no significant difference was found between groups. I2 supplementation enhances the antineoplastic effect in mDOX, exhibiting a significant decrease in the tumor epithelial fraction, diminished expression of chemoresistance (MDR1 and Survivin) and invasion (uPA) markers and enhanced expression of the differentiation factor known as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors type gamma (PPARγ). Significant tumor lymphocytic infiltration was also observed in both I2-supplemented groups. The ten-month survival analysis showed that the entire I2 supplementation (before and after surgery) induced 67-73% of disease-free survival, whereas supplementation in the last period (only after surgery) produced 50% in both schemes.
Conclusions: The mDOX+I2 scheme improves the therapeutic outcome, diminishes the invasive capacity, attenuates the adverse events and increases disease-free survival. These data led us to propose mDOX+I2 as an effective treatment for canine mammary cancer.
Keywords: Animal welfare; Canine mammary cancer; Doxorubicin; Molecular iodine; Neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Iodine and doxorubicin, a good combination for mammary cancer treatment: antineoplastic adjuvancy, chemoresistance inhibition, and cardioprotection.Mol Cancer. 2013 May 24;12:45. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-45. Mol Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23705792 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular iodine impairs chemoresistance mechanisms, enhances doxorubicin retention and induces downregulation of the CD44+/CD24+ and E-cadherin+/vimentin+ subpopulations in MCF-7 cells resistant to low doses of doxorubicin.Oncol Rep. 2017 Nov;38(5):2867-2876. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5934. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28901484
-
Molecular iodine exerts antineoplastic effects by diminishing proliferation and invasive potential and activating the immune response in mammary cancer xenografts.BMC Cancer. 2019 Mar 22;19(1):261. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5437-3. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30902074 Free PMC article.
-
6-iodolactone, key mediator of antitumoral properties of iodine.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2014 Aug;112:27-33. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2014.07.001. Epub 2014 Jul 10. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2014. PMID: 25018052 Review.
-
Liposome-enhanced tumour therapy in canine mammary gland tumours.Tijdschr Diergeneeskd. 1993 Mar;118 Suppl 1:32S-33S. Tijdschr Diergeneeskd. 1993. PMID: 8480312 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Non-Exosomal and Exosome-Derived miRNAs as Promising Biomarkers in Canine Mammary Cancer.Life (Basel). 2022 Apr 1;12(4):524. doi: 10.3390/life12040524. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Alterations in Canine Mammary Tumors.Animals (Basel). 2023 Aug 30;13(17):2757. doi: 10.3390/ani13172757. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37685021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of mammary gland tumors in bitches: effects of sodium dichloroacetate as neoadjuvant therapy.J Vet Med Sci. 2024 Jun 19;86(6):677-683. doi: 10.1292/jvms.23-0393. Epub 2024 May 1. J Vet Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38692860 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant Effect of Molecular Iodine in Conventional Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer. Randomized Pilot Study.Nutrients. 2019 Jul 17;11(7):1623. doi: 10.3390/nu11071623. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31319484 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Molecular Iodine Has Extrathyroidal Effects as an Antioxidant, Differentiator, and Immunomodulator.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 27;22(3):1228. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031228. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33513754 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lavalle GE, De Campos CB, Bertagnolli AC, Cassali GD. Canine malignant mammary gland neoplasm with advanced clinical staging treated with carboplatin and cyclooxygenase innibitors. In Vivo. 2012;26:375–379. - PubMed
-
- Arenas C, Peña L, Granados-Soler JL, Pérez-Alenza MD. Adjuvant therapy for highly malignant canine mammary tumours: Cox-2 inhibitor versus chemotherapy: a case-control prospective study. Vet Rec. 2016; 10.1136/vr.103398. - PubMed
-
- Karayannopoulou M, Lafioniatis S. Recent advances on canine mammary cancer chemotherapy : a review of studies from 2000 to date. Revue Med Vet. 2016;167:192–200.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

