LncRNA-TUSC7/miR-224 affected chemotherapy resistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by competitively regulating DESC1
- PMID: 29530057
- PMCID: PMC5848549
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-018-0724-4
LncRNA-TUSC7/miR-224 affected chemotherapy resistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by competitively regulating DESC1
Abstract
Background: This study aims to clarify the underlying mechanism for the tumor suppressive function of lnc TUSC7 in chemotherapy resistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
Methods: TUSC7, miR-224 and DESC1 expressions in ESCC tissues and cells were detected by qRT-PCR. Protein level of DESC1, EGFR and p-AKT were observed by Western blot. Overall survival was calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method. Dual-luciferase reporter gene assay and RIP assay were used to comfirm TUSC7 binding to miR-224, and miR-224 binding to DESC1. Cell proliferation, apoptosis, and colony formation was detected by MTT, Flow Cytometry and Colony formation assays.
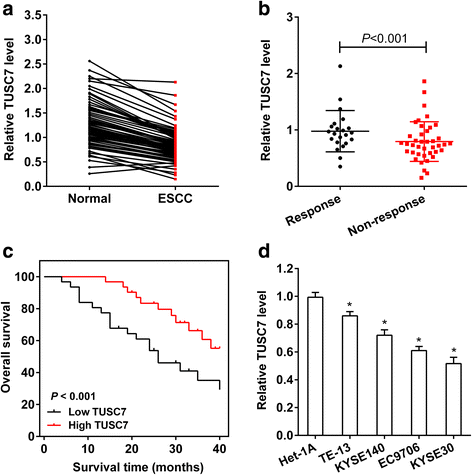
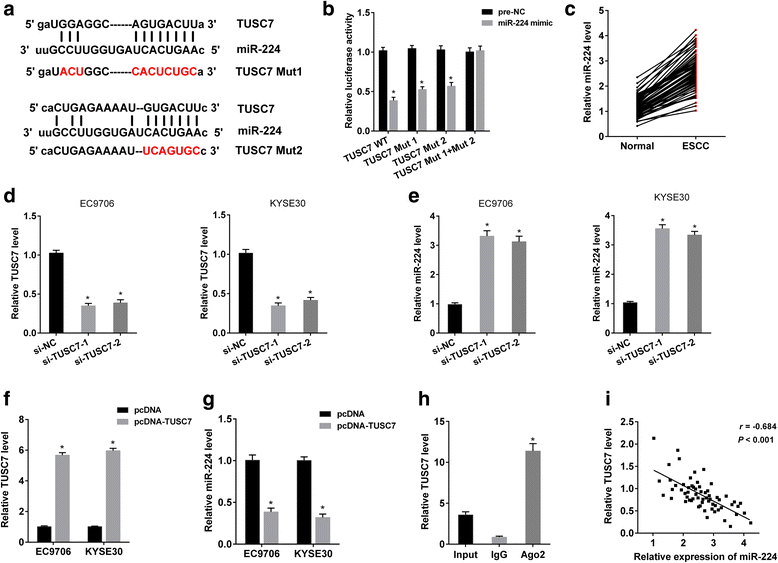
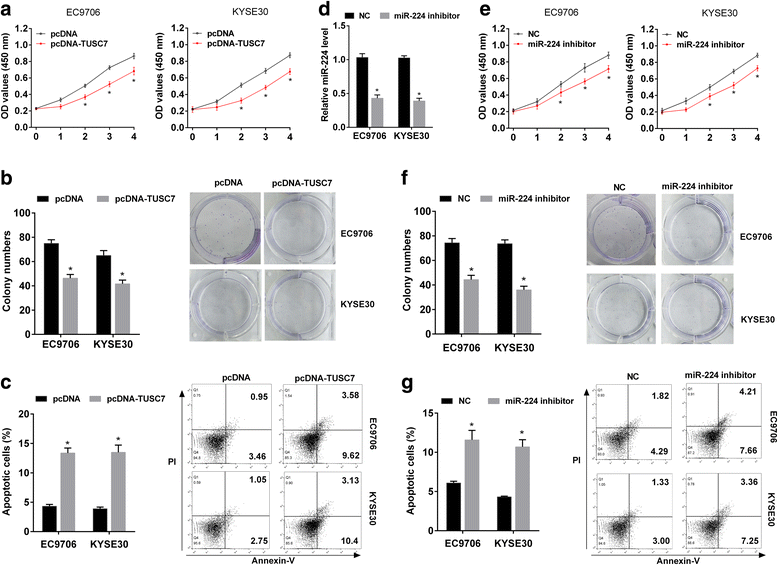
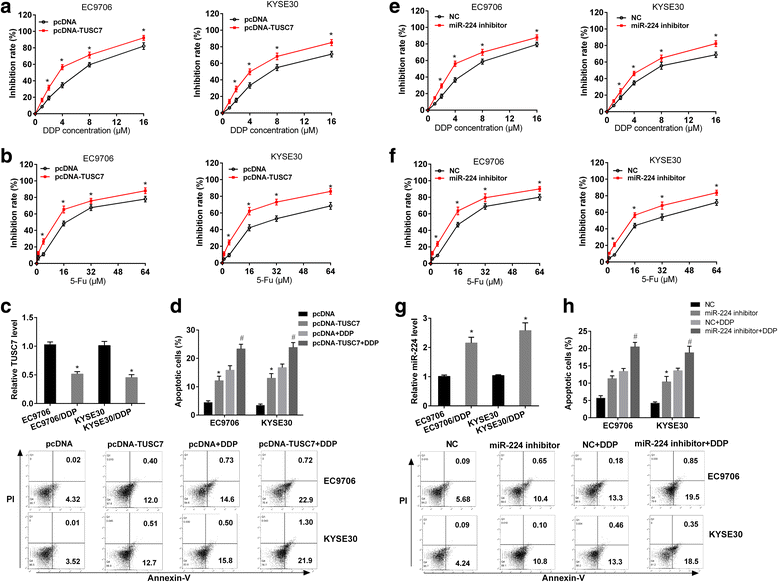
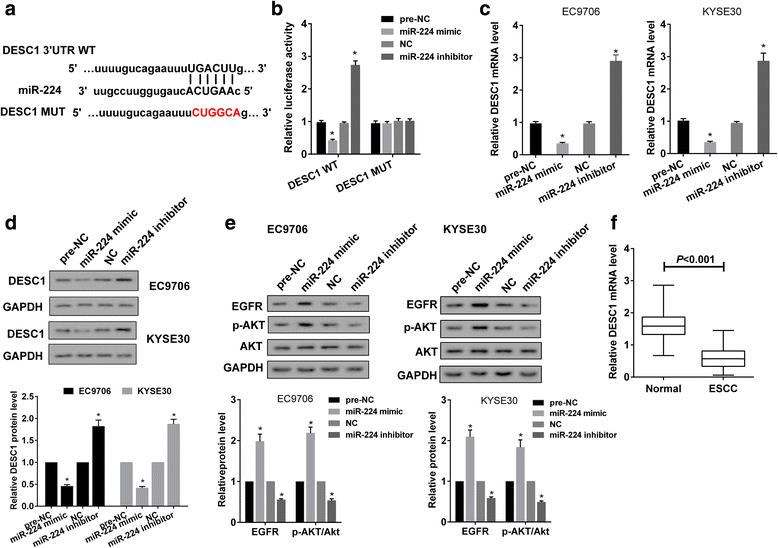
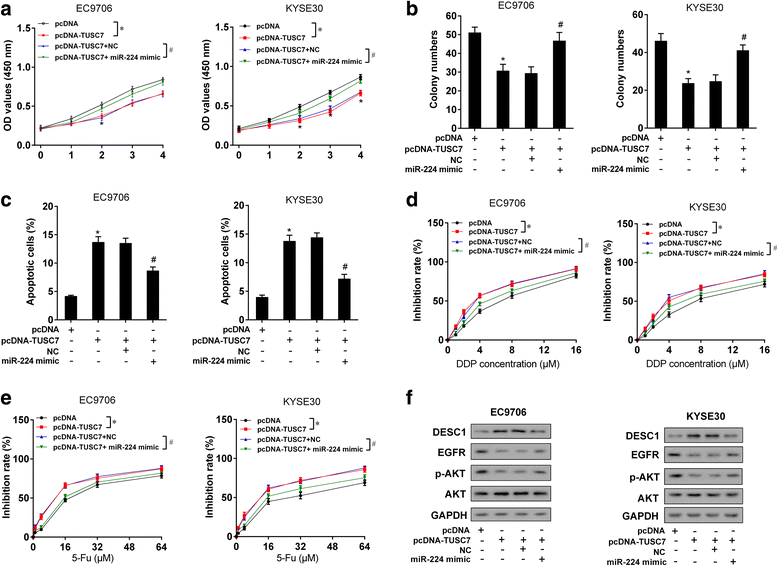
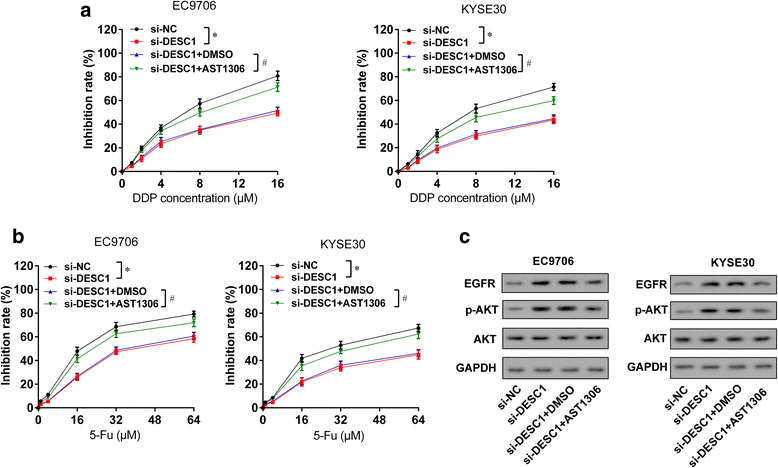
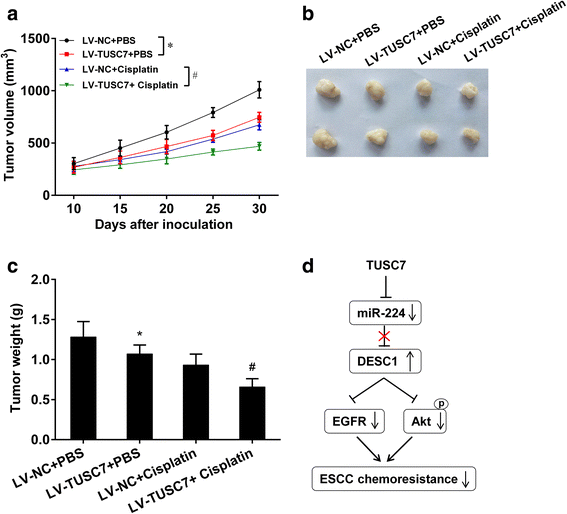
Results: TUSC7 was downregulated in ESCC tissues and cells, and low TUSC7 indicated worse overall survival. The analysis of bioinformatics softwares showed that TUSC7 specifically bound to miR-224, and we proved miR-224 was upregulated in ESCC and negatively correlated with TUSC7 expression. Overexpression of TUSC7/inhibition of miR-224 suppressed cell proliferation, colony formation and chemotherapy resistance of ESCC cells, and promoted cell apoptosis. In addition, we confirmed that miR-224 specifically bound to DESC1, and negatively correlated with DESC1. TUSC7 suppressed the proliferation and chemotherapy resistance of ESCC cells by increasing DESC1 expression via inhibiting miR-224. We also confirmed DESC1 inhibited chemotherapy resistance of ESCC cells via EGFR/AKT. Finally, in vivo experiments demonstrated that overexpression of TUSC7 decreased tumor growth and chemotherapy resistance.
Conclusion: These findings suggested TUSC7 suppressed chemotherapy resistance of ESCC by downregulating miR-224 to modulate DESC1/EGFR/AKT pathway.
Keywords: Chemotherapy resistance; DESC1; Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; TUSC7; miR-224.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by Ethics Committee of Zhengzhou University, and informed consent was obtained from each patient. Animal studies were approved by the Ethics Committee of Animal Experiments of Zhengzhou University.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
lncTUG1/miR-144-3p affect the radiosensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by competitively regulating c-MET.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Jan 9;39(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1519-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 31918742 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA NORAD/miR-224-3p/MTDH axis contributes to CDDP resistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by promoting nuclear accumulation of β-catenin.Mol Cancer. 2021 Dec 10;20(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01455-y. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34893064 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA circNTRK2 facilitates the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through up-regulating NRIP1 expression via miR-140-3p.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Jul 11;39(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01640-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32653032 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of long non‑coding RNAs in esophageal cell squamous carcinoma (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2024 Aug;54(2):72. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5396. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Int J Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38963019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 30;21(1):258. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010258. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31905958 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long Noncoding RNA MLK7-AS1 Promotes Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Migration and Invasion via the miR-375-3p/YWHAZ Axis.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 22;11:626036. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.626036. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33968726 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Long Non-coding RNA to Therapeutically Regulate Gene Expression in Cancer.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Sep 4;21:712-724. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.07.005. Epub 2020 Jul 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 32771923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of the Six-lncRNA Prognosis Signature as a Novel Biomarker in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 31;13:839589. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.839589. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35432441 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of long noncoding RNA breast cancer anti-estrogen resistance 4 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion, and migration in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the microRNA-181c-5p/LIM and SH3 protein 1 axis.Bioengineered. 2022 May;13(5):12998-13010. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2060720. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35611706 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000277 promotes tumor progression and DDP resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2022 Mar 4;22(1):238. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09241-9. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35241028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen J, et al. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy combined with paclitaxel and platinum treatment regimens in locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol. 2018;20(3):411–19. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama Y, et al. Investigation of operative outcomes of thoracoscopic esophagectomy after triplet chemotherapy with docetaxel, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil for advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Surg Endosc. 2018;32(1):391–9. - PubMed
-
- Yen YC, et al. Effectiveness of esophagectomy in patients with thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma receiving definitive radiotherapy or concurrent chemoradiotherapy through intensity-modulated radiation therapy techniques. Cancer. 2017;123(11):2043–2053. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30565. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

