Inhibition of CREB binding protein-beta-catenin signaling down regulates CD133 expression and activates PP2A-PTEN signaling in tumor initiating liver cancer cells
- PMID: 29530069
- PMCID: PMC5848530
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-018-0222-5
Inhibition of CREB binding protein-beta-catenin signaling down regulates CD133 expression and activates PP2A-PTEN signaling in tumor initiating liver cancer cells
Abstract
Background: The WNT-beta-catenin pathway is known to regulate cellular homeostasis during development and tissue regeneration. Activation of WNT signaling increases the stability of cytoplasmic beta-catenin and enhances its nuclear translocation. Nuclear beta-catenin function is regulated by transcriptional co-factors such as CREB binding protein (CBP) and p300. Hyper-activated WNT-beta-catenin signaling is associated with many cancers. However, its role in inducing stemness to liver cancer cells, its autoregulation and how it regulates tumor suppressor pathways are not well understood. Here we have investigated the role of CBP-beta-catenin signaling on the expression of CD133, a known stem cell antigen and PP2A-PTEN pathway in tumor initiating liver cancer cells.
Methods: Human hepatoblastoma cell line HepG2 and clonally expanded CD133 expressing tumor initiating liver cells (TICs) from premalignant murine liver were used in this study. CBP-beta-catenin inhibitor ICG001 was used to target CBP-beta catenin signaling in liver cancer cells in vitro. Western blotting and real time PCR (qPCR) were used to quantify protein expression/phosphorylation and mRNA levels, respectively. CBP and CD133 gene silencing was performed by siRNA transfection. Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) was performed to quantify CD133 positive cells. Protein Phosphatase (PP2A) activity was measured after PP2AC immunoprecipitation.
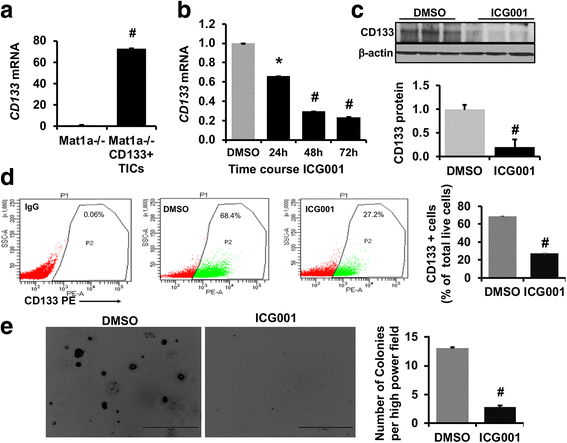
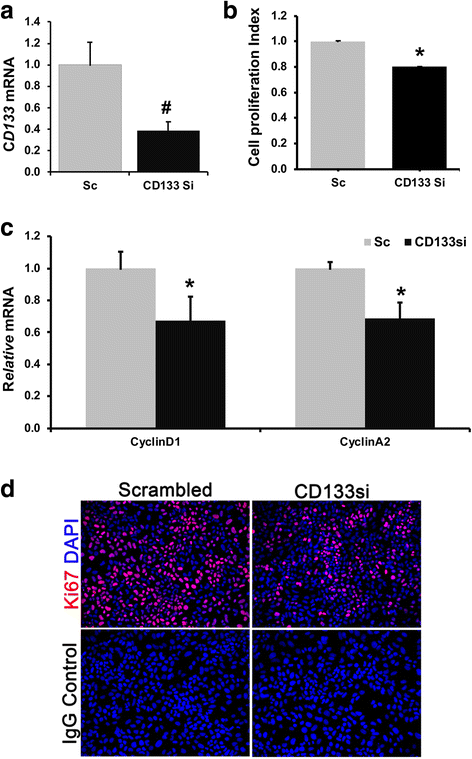
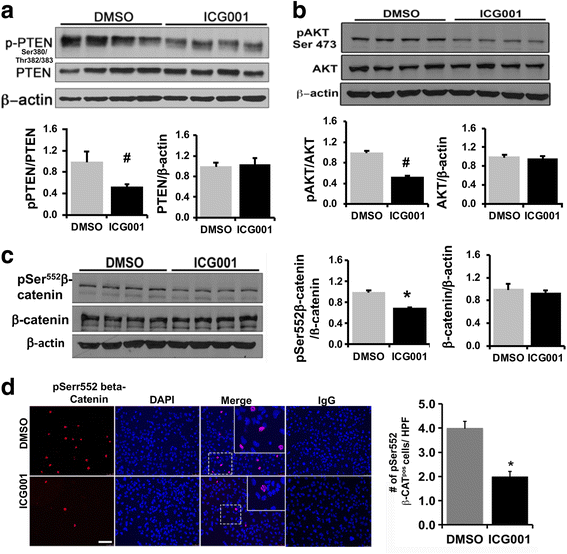
Results: CBP inhibitor ICG001 and CBP silencing significantly reduced CD133 expression and anchorage independent growth in HepG2 and murine TICs. CD133 silencing in TICs decreased cell proliferation and expression levels of cell cycle regulatory genes, CyclinD1 and CyclinA2. ICG001 treatment and CBP silencing reduced the levels of phosphoSer380/Tyr382/383PTEN, phosphoSer473-AKT, Phospho-Ser552beta-catenin in TICs. ICG001 mediated de-phosphorylation of PTEN in TICs was PP2A dependent and partly prevented by co-treatment with PP2A inhibitor okadaic acid.
Conclusions: CBP-beta-catenin signaling promotes stemness via CD133 induction and cell proliferation in TICs. We found a novel functional link between CBP-beta-catenin and PP2A-PTEN-AKT pathway in liver TICs. Therefore, CBP-beta-catenin-PP2A-PTEN-AKT signaling axis could be a novel therapeutic target to prevent liver tumor initiation and cancer recurrence.
Keywords: CBP; CD133; Cancer stem cells; PP2A; PTEN; Tumor initiating cells; WNT-beta catenin signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

