Association of Vancomycin MIC and Molecular Characteristics with Clinical Outcomes in Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus Acute Hematogenous Osteoarticular Infections in Children
- PMID: 29530845
- PMCID: PMC5923104
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00084-18
Association of Vancomycin MIC and Molecular Characteristics with Clinical Outcomes in Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus Acute Hematogenous Osteoarticular Infections in Children
Abstract
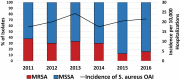
Strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), particularly those belonging to the USA300 pulsotype, have been well described to cause severe osteoarticular infections (OAIs). A vancomycin MIC of ≥1.5 μg/ml has been demonstrated to contribute to disease severity in adults with MRSA and even methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) bacteremia. Little data exist describing the outcomes of MSSA OAIs in terms of molecular characteristics and vancomycin MIC. All patients/isolates were chosen from a surveillance study at Texas Children's Hospital (TCH). S. aureus OAI isolates were identified from 2011 to 2016 and subjected to vancomycin Etests, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE), and PCR to determine Panton-Valentine leucocidin (PVL) production and agr group. Two hundred fifty-two cases of S. aureus OAI were identified; 183 cases were MSSA (72.6%). During the study period, a decrease in the proportion of cases secondary to MRSA was observed, declining from 37.8% to 15.9% (P = 0.02). Of the MSSA isolates, 26.2% and 23.5% were USA300 and PVL positive, respectively. An increase in the proportion of MSSA isolates with a vancomycin MIC of ≥1.5 μg/ml occurred in the study period (P = 0.004). In MSSA, an elevated vancomycin MIC was associated with multiple surgical procedures and venous thromboses, even when adjusting for empirical β-lactam use. An increase in vancomycin MIC was noted among isolates belonging to agr group 4 during the study period. Methicillin resistance is declining among S. aureus OAI isolates at TCH. Simultaneously, vancomycin Etest MICs are increasing among MSSA isolates. Vancomycin MICs of ≥2 μg/ml are associated with adverse clinical outcomes in MSSA irrespective of antibiotic choice, suggesting that this may be a surrogate for organism virulence.
Keywords: Etest; MRSA; MSSA; osteomyelitis; pediatric; vancomycin.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

References
-
- Klevens RM, Morrison MA, Nadle J, Petit S, Gershman K, Ray S, Harrison LH, Lynfield R, Dumyati G, Townes JM, Craig AS, Zell ER, Fosheim GE, McDougal LK, Carey RB, Fridkin SK, Active Bacterial Core Surveillance (ABCs) MRSA Investigators. 2007. Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the United States. JAMA 298:1763–1771. doi: 10.1001/jama.298.15.1763. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2015. Active bacterial core surveillance report, Emerging Infections Program Network, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, 2015. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA.
-
- Hultén KG, Mason EO, Lamberth LB, Forbes AR, Revell PA, Kaplan SL. 2018. Analysis of invasive community-acquired methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus infections during a period of declining CA-MRSA infections at a large children's hospital. Pediatr Infect Dis J 37:235–241. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000001753. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

