Meta Salud Diabetes study protocol: a cluster-randomised trial to reduce cardiovascular risk among a diabetic population of Mexico
- PMID: 29530914
- PMCID: PMC5857644
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-020762
Meta Salud Diabetes study protocol: a cluster-randomised trial to reduce cardiovascular risk among a diabetic population of Mexico
Abstract
Introduction: Northern Mexico has among the highest rates of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and diabetes in the world. This research addresses core gaps in implementation science to develop, test and scale-up CVD risk-reduction interventions in diabetics through a national primary care health system.
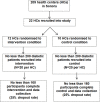
Methods and analysis: The Meta Salud Diabetes (MSD) research project is a parallel two-arm cluster-randomised clinical behavioural trial based in 22 (n=22) health centres in Sonora, Mexico. MSD aims to evaluate the effectiveness of the MSD intervention for the secondary prevention of CVD risk factors among a diabetic population (n=320) compared with the study control of usual care. The MSD intervention consists of 2-hour class sessions delivered over a 13-week period providing educational information to encourage sustainable behavioural change to prevent disease complications including the adoption of physical activity. MSD is delivered within the context of Mexico's national primary care health centre system by health professionals, including nurses, physicians and community health workers via existing social support groups for individuals diagnosed with chronic disease. Mixed models are used to estimate the effect of MSD by comparing cardiovascular risk, as measured by the Framingham Risk Score, between the trial arms. Secondary outcomes include hypertension, behavioural risk factors and psychosocial factors.
Ethics and dissemination: This work is supported by the National Institutes of Health, National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (1R01HL125996-01) and approved by the University of Arizona Research Institutional Review Board (Protocol 1508040144) and the Research Bioethics Committee at the University of Sonora. The first Internal Review Board approval date was 31 August 2015 with five subsequent approved amendments. This article refers to protocol V.0.2, dated 30 January 2017. Results will be disseminated via peer-reviewed publication and presentation at international conferences and will be shared through meetings with health systems officials.
Trial registration number: NCT0280469; Pre-results.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02804698.
Keywords: coronary heart disease; general diabetes; public health.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Sistema Nacional de Información en Salud. Principales causes de mortalidad general, 2008. 2008. http://sinais.salud.gob.mx/mortalidad.
-
- Gutiérrez J, Rivera-Dommarco J, Shamah-Levy T, et al. . Encuesta Nacional de Salud y Nutricion2012: resultados nacionales. México: Instituto Nacional de Salud Pública, 2012.
-
- Pan American Health Organization (PAHO). Health in the Americas: 2012 edition. México, Washington: Pan American Health Organization, 2012.
-
- Secretaria de Salud. Boletín de información estadística 2014-2015. 2015 http://www.dgis.salud.gob.mx/descargas/pdf/Boletxn_InformacixnEstadxstic...
-
- Secretaria de Salud. Programa nacional de salud 2007-2012. Mexico D.F, 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical