Transmission and Epidemiology of Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 and 4 Infections
- PMID: 29530946
- PMCID: PMC6211381
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a032144
Transmission and Epidemiology of Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 and 4 Infections
Abstract
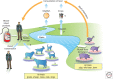
Following the introduction of robust serological and molecular tools, our understanding of the epidemiology of zoonotic hepatitis E virus (HEV) has improved considerably in recent years. Current thinking suggests that consumption of pork meat products is the key route of infection in humans, but it is certainly not the only one. Other routes of infection include environmental spread, contaminated water, and via the human blood supply. The epidemiology of HEV genotype (gt)3 and gt4 is complex, as there are several sources and routes of infection, and it is likely that these vary between and within countries and over time.
Copyright © 2018 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abravanel F, Lhomme S, Chapuy-Regaud S, Mansuy JM, Muscari F, Sallusto F, Rostaing L, Kamar N, Izopet J. 2014. Hepatitis E virus reinfections in solid-organ-transplant recipients can evolve into chronic infections. J Infect Dis 209: 1900–1906. - PubMed
-
- Abravanel F, Lhomme S, Chapuy-Regaud S, Peron JM, Alric L, Rostaing L, Kamar N, Izopet J. 2015. Performance of a new rapid test for detecting anti-hepatitis E virus immunoglobulin M in immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients. J Clin Virol 70: 101–104. - PubMed
-
- Abravanel F, Goutagny N, Perret C, Lhomme S, Vischi F, Aversenq A, Chapel A, Dehainault N, Piga N, Dupret-Carruel J, et al. 2017a. Evaluation of two VIDAS prototypes for detecting anti-HEV IgG. J Clin Virol 89: 46–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
