Efficient molecular evolution to generate enantioselective enzymes using a dual-channel microfluidic droplet screening platform
- PMID: 29531246
- PMCID: PMC5847605
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-03492-6
Efficient molecular evolution to generate enantioselective enzymes using a dual-channel microfluidic droplet screening platform
Abstract
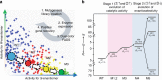
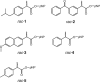
Directed evolution has long been a key strategy to generate enzymes with desired properties like high selectivity, but experimental barriers and analytical costs of screening enormous mutant libraries have limited such efforts. Here, we describe an ultrahigh-throughput dual-channel microfluidic droplet screening system that can be used to screen up to ~107 enzyme variants per day. As an example case, we use the system to engineer the enantioselectivity of an esterase to preferentially produce desired enantiomers of profens, an important class of anti-inflammatory drugs. Using two types of screening working modes over the course of five rounds of directed evolution, we identify (from among 5 million mutants) a variant with 700-fold improved enantioselectivity for the desired (S)-profens. We thus demonstrate that this screening platform can be used to rapidly generate enzymes with desired enzymatic properties like enantiospecificity, chemospecificity, and regiospecificity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Improved enantioselectivity of thermostable esterase from Archaeoglobus fulgidus toward (S)-ketoprofen ethyl ester by directed evolution and characterization of mutant esterases.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Aug;99(15):6293-301. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6422-7. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25661815
-
[Directed evolution of Thermophilic esterase from the archaeon Aeropyrum pemix K1].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2006 Apr;46(2):259-62. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2006. PMID: 16736588 Chinese.
-
An improved single cell ultrahigh throughput screening method based on in vitro compartmentalization.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 24;9(2):e89785. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089785. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24587033 Free PMC article.
-
Improved biocatalysts by directed evolution and rational protein design.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2001 Apr;5(2):137-43. doi: 10.1016/s1367-5931(00)00182-4. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2001. PMID: 11282339 Review.
-
Droplet-based microfluidics and enzyme evolution.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2024 Jun;87:103097. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2024.103097. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38430713 Review.
Cited by
-
Droplet-based microfluidic platform for high-throughput screening of Streptomyces.Commun Biol. 2021 May 31;4(1):647. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02186-y. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34059751 Free PMC article.
-
Droplet Microfluidics and Directed Evolution of Enzymes: An Intertwined Journey.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021 Nov 8;60(46):24368-24387. doi: 10.1002/anie.202016154. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021. PMID: 33539653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Massively parallel genetic perturbation suggests the energetic structure of an amyloid-β transition state.Sci Adv. 2025 Jun 13;11(24):eadv1422. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adv1422. Epub 2025 Jun 11. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40498820 Free PMC article.
-
A High-Throughput Screening System Based on Droplet Microfluidics for Glucose Oxidase Gene Libraries.Molecules. 2020 May 22;25(10):2418. doi: 10.3390/molecules25102418. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32455903 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Residue at Position 2 in the Catalytic Activity of AA9 Lytic Polysaccharide Monooxygenases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 5;24(9):8300. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098300. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37176008 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

