Learning by neural reassociation
- PMID: 29531364
- PMCID: PMC5876156
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-018-0095-3
Learning by neural reassociation
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Learning by neural reassociation.Nat Neurosci. 2018 Aug;21(8):1138. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0185-2. Nat Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29976964
Abstract
Behavior is driven by coordinated activity across a population of neurons. Learning requires the brain to change the neural population activity produced to achieve a given behavioral goal. How does population activity reorganize during learning? We studied intracortical population activity in the primary motor cortex of rhesus macaques during short-term learning in a brain-computer interface (BCI) task. In a BCI, the mapping between neural activity and behavior is exactly known, enabling us to rigorously define hypotheses about neural reorganization during learning. We found that changes in population activity followed a suboptimal neural strategy of reassociation: animals relied on a fixed repertoire of activity patterns and associated those patterns with different movements after learning. These results indicate that the activity patterns that a neural population can generate are even more constrained than previously thought and might explain why it is often difficult to quickly learn to a high level of proficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


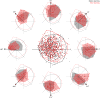

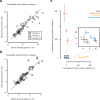

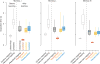
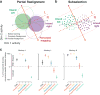
Comment in
-
Set in one's thoughts.Nat Neurosci. 2018 Apr;21(4):459-460. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0105-5. Nat Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29531363 No abstract available.
References
-
- Asaad WF, Rainer G, Miller EK. Neural activity in the primate prefrontal cortex during associative learning. Neuron. 1998;21(6):1399–1407. - PubMed
-
- Li CSR, Padoa-Schioppa C, Bizzi E. Neuronal correlates of motor performance and motor learning in the primary motor cortex of monkeys adapting to an external force field. Neuron. 2001;30(2):593–607. - PubMed
-
- Paz R, Boraud T, Natan C, Bergman H, Vaadia E. Preparatory activity in motor cortex reflects learning of local visuomotor skills. Nature neuroscience. 2003;6(8):882–890. - PubMed
-
- Rokni U, Richardson AG, Bizzi E, Seung HS. Motor learning with unstable neural representations. Neuron. 2007;54(4):653–666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

