Improved Left Ventricular Aneurysm Repair with Cell- and Cytokine-Seeded Collagen Patches
- PMID: 29531539
- PMCID: PMC5831860
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/4717802
Improved Left Ventricular Aneurysm Repair with Cell- and Cytokine-Seeded Collagen Patches
Abstract
Background: Engineered heart tissues (EHTs) present a promising alternative to current materials for surgical ventricular restoration (SVR); however, the clinical application remains limited by inadequate vascularization postimplantation. Moreover, a suitable and economic animal model for primary screening is another important issue.
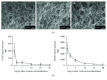
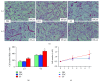
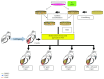
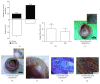
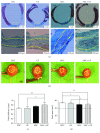
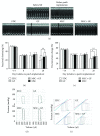
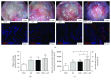
Methods: Recently, we used 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride chemistry (EDC) to initiate a strengthened, cytokine-conjugated collagenous platform with a controlled degradation speed. In vitro, the biomaterial exhibited an enhanced mechanical strength maintaining a porous ultrastructure, and the constant release of cytokines promoted the proliferation of seeded human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs). In vivo, with the hMSC-seeded, cytokine-immobilized patch (MSCs + GF patch), we performed modified SVR for rats with left ventricular aneurysm postmyocardial infarction (MI). Overall, the rats that underwent modified SVR lost less blood and had lower mortality. After 4 weeks, the rats repaired with this cell-seeded, cytokine-immobilized patch presented preserved cardiac function, beneficial morphology, enhanced cell infiltration, and functional vessel formation compared with the cytokine-free (MSC patch), cell-free (GF patch), or blank controls (EDC patch). Furthermore, the degradable period of the collagen patch in vivo extended up to 3 months after EDC treatment.
Conclusions: EDC may substantially modify collagen scaffold and provide a promising and practical biomaterial for SVR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aged human cells rejuvenated by cytokine enhancement of biomaterials for surgical ventricular restoration.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012 Nov 20;60(21):2237-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.08.985. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 23153846
-
Surgical ventricular restoration with a cell- and cytokine-seeded biodegradable scaffold.Biomaterials. 2010 Oct;31(30):7684-94. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.06.048. Epub 2010 Jul 24. Biomaterials. 2010. PMID: 20659765
-
Chitosan/silk fibroin modified nanofibrous patches with mesenchymal stem cells prevent heart remodeling post-myocardial infarction in rats.Acta Biomater. 2018 Oct 15;80:154-168. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.09.013. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 30218777
-
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Patients with Cyanotic Congenital Heart Disease are Optimal Candidate for Cardiac Tissue Engineering.Biomaterials. 2020 Feb;230:119574. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119574. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Biomaterials. 2020. PMID: 31761487
-
Repairing chronic myocardial infarction with autologous mesenchymal stem cells engineered tissue in rat promotes angiogenesis and limits ventricular remodeling.J Biomed Sci. 2012 Nov 12;19(1):93. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-19-93. J Biomed Sci. 2012. PMID: 23146158 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Review Insights In Cardiac Tissue Engineering: Cells, Scaffolds, and Pharmacological Agents.Iran J Pharm Res. 2021 Fall;20(4):467-496. doi: 10.22037/IJPR.2021.114730.15012. Iran J Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 35194460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Possible Treatment of Myocardial Infarct Based on Tissue Engineering Using a Cellularized Solid Collagen Scaffold Functionalized with Arg-Glyc-Asp (RGD) Peptide.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 22;22(22):12563. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212563. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Biomaterials: The Perfect Match for Cardiac Repair?Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 19;19(10):3236. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103236. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30347686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of mesenchymal stem cells and three-dimensional collagen scaffold preserves ventricular remodeling in rat myocardial infarction model.World J Stem Cells. 2022 Aug 26;14(8):633-657. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i8.633. World J Stem Cells. 2022. PMID: 36157910 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem/Progenitor Cells: The Prospect of Human Clinical Translation.Stem Cells Int. 2020 Aug 11;2020:8837654. doi: 10.1155/2020/8837654. eCollection 2020. Stem Cells Int. 2020. PMID: 33953753 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Horii T., Tambara K., Nishimura K., Suma H., Komeda M. Residual fibrosis affects a long-term result of left ventricular volume reduction surgery for dilated cardiomyopathy in a rat experimental study. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery. 2004;26(6):1174–1179. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2004.06.023. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

