Diffusion-weighted imaging characteristics of methotrexate-induced acute encephalopathy
- PMID: 29531719
- PMCID: PMC5838264
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.1376
Diffusion-weighted imaging characteristics of methotrexate-induced acute encephalopathy
Abstract
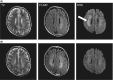
Methotrexate (MTX)-induced encephalopathy is a grave complication in patients with malignancies. The early diagnosis of acute encephalopathy was difficult by conventional computed tomography (CT), and T1- or T2-weighted magnet resonance (MR) imaging. We report that the diffusion-weighted (DW) imaging is useful for early detection of acute leukoencephalopathy.
Keywords: Diffusion‐weighted imaging; encephalopathy; magnetic resonance imaging; methotrexate; neurotoxicity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute methotrexate neurotoxicity: findings on diffusion-weighted imaging and correlation with clinical outcome.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004 Nov-Dec;25(10):1688-95. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004. PMID: 15569732 Free PMC article.
-
Methotrexate-induced acute toxic leukoencephalopathy.J Cancer Res Ther. 2012 Apr-Jun;8(2):292-6. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.98993. J Cancer Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 22842379
-
Transient encephalopathy after intrathekal methotrexate chemotherapy: diffusion-weighted MRI.J Neurooncol. 2005 May;73(1):47-9. doi: 10.1007/s11060-004-2929-y. J Neurooncol. 2005. PMID: 15933817
-
Diffusion-weighted MR of the brain: methodology and clinical application.Radiol Med. 2005 Mar;109(3):155-97. Radiol Med. 2005. PMID: 15775887 Review. English, Italian.
-
Acute Leukoencephalopathy with Restricted Diffusion.Indian J Crit Care Med. 2018 Jul;22(7):519-523. doi: 10.4103/ijccm.IJCCM_139_18. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2018. PMID: 30111927 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Differential diagnoses of ischemic stroke using imaging].Radiologe. 2019 Jul;59(7):627-631. doi: 10.1007/s00117-019-0557-y. Radiologe. 2019. PMID: 31201515 Review. German.
References
-
- Filley, C. M. , and Kleinschmidt‐DeMasters B. K.. 2001. Toxic leukoencephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 345:425–432. - PubMed
-
- Haykin, M. E. , Gorman M., van Hoff J., Fulbright R. K., and Baehring J. M.. 2006. Diffusion‐weighted MRI correlates of subacute methotrexate‐related neurotoxicity. J. Neurooncol. 76:153–157. - PubMed
-
- Bleyer, W. A. 1978. The clinical pharmacology of methotrexate: new applications of an old drug. Cancer 41:36–51. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

