Surveillance nanotechnology for multi-organ cancer metastases
- PMID: 29531851
- PMCID: PMC5844578
- DOI: 10.1038/s41551-017-0167-9
Surveillance nanotechnology for multi-organ cancer metastases
Abstract
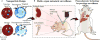
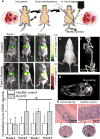
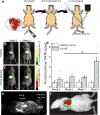
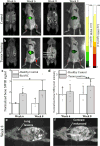
The identification and molecular profiling of early metastases remains a major challenge in cancer diagnostics and therapy. Most in vivo imaging methods fail to detect small cancerous lesions, a problem that is compounded by the distinct physical and biological barriers associated with different metastatic niches. Here, we show that intravenously injected rare-earth-doped albumin-encapsulated nanoparticles emitting short-wave infrared light (SWIR) can detect targeted metastatic lesions in vivo, allowing for the longitudinal tracking of multi-organ metastases. In a murine model of basal human breast cancer, the nanoprobes enabled whole-body SWIR detection of adrenal gland microlesions and bone lesions that were undetectable via contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (CE-MRI) as early as, respectively, three weeks and five weeks post-inoculation. Whole-body SWIR imaging of nanoprobes functionalized to differentially target distinct metastatic sites and administered to a biomimetic murine model of human breast cancer resolved multi-organ metastases that showed varied molecular profiles at the lungs, adrenal glands and bones. Real-time surveillance of lesions in multiple organs should facilitate pre-therapy and post-therapy monitoring in preclinical settings.
Keywords: cancer metastasis; nanotechnology; rare earths; shortwave infrared imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
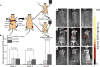
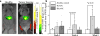

Similar articles
-
Shortwave infrared emitting multicolored nanoprobes for biomarker-specific cancer imaging in vivo.BMC Cancer. 2020 Nov 10;20(1):1082. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07604-8. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33172421 Free PMC article.
-
Shortwave Infrared-Emitting Theranostics for Breast Cancer Therapy Response Monitoring.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Oct 6;7:569415. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.569415. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33134314 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR-4 Targeted, Short Wave Infrared (SWIR) Emitting Nanoprobes for Enhanced Deep Tissue Imaging and Micrometastatic Cancer Lesion Detection.Small. 2015 Dec 16;11(47):6347-57. doi: 10.1002/smll.201502202. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Small. 2015. PMID: 26514367 Free PMC article.
-
Animal models of bone metastasis.Cancer. 2003 Feb 1;97(3 Suppl):748-57. doi: 10.1002/cncr.11150. Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12548572 Review.
-
Preoperative imaging in renal cell cancer.World J Urol. 2004 Nov;22(5):307-15. doi: 10.1007/s00345-004-0411-2. Epub 2004 Jul 30. World J Urol. 2004. PMID: 15290202 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering Tumor-Targeting Nanoparticles as Vehicles for Precision Nanomedicine.Med One. 2019;4:e190021. doi: 10.20900/mo.20190021. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Med One. 2019. PMID: 31592196 Free PMC article.
-
Early Detection of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in the Lung Pre-Metastatic Niche by Shortwave Infrared Nanoprobes.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Apr 17;16(4):549. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16040549. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38675210 Free PMC article.
-
Shortwave infrared emitting multicolored nanoprobes for biomarker-specific cancer imaging in vivo.BMC Cancer. 2020 Nov 10;20(1):1082. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07604-8. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33172421 Free PMC article.
-
A stable and biocompatible shortwave infrared nanoribbon for dual-channel in vivo imaging.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 2;16(1):4. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55445-x. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39747028 Free PMC article.
-
Scalable Signature-Based Molecular Diagnostics Through On-chip Biomarker Profiling Coupled with Machine Learning.Ann Biomed Eng. 2020 Oct;48(10):2377-2399. doi: 10.1007/s10439-020-02593-y. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Ann Biomed Eng. 2020. PMID: 32816167 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

