Dealloyed Intra-Nanogap Particles with Highly Robust, Quantifiable Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Signals for Biosensing and Bioimaging Applications
- PMID: 29532028
- PMCID: PMC5833005
- DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.7b00584
Dealloyed Intra-Nanogap Particles with Highly Robust, Quantifiable Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Signals for Biosensing and Bioimaging Applications
Abstract
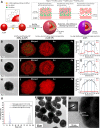
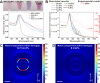
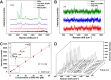
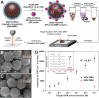
Uniformly controlling a large number of metal nanostructures with a plasmonically enhanced signal to generate quantitative optical signals and the widespread use of these structures for surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)-based biosensing and bioimaging applications are of paramount importance but are extremely challenging. Here, we report a highly controllable, facile selective-interdiffusive dealloying chemistry for synthesizing the dealloyed intra-nanogap particles (DIPs) with a ∼2 nm intragap in a high yield (∼95%) without the need for an interlayer. The SERS signals from DIPs are highly quantitative and polarization-independent with polarized laser sources. Remarkably, all the analyzed particles displayed the SERS enhancement factors (EFs) of ≥1.1 × 108 with a very narrow distribution of EFs. Finally, we show that DIPs can be used as ultrasensitive SERS-based DNA detection probes for detecting 10 aM to 1 pM target concentrations and highly robust, quantitative real-time cell imaging probes for long-term imaging with low laser power and short exposure time.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Plasmonic Nanogap-Enhanced Raman Scattering with Nanoparticles.Acc Chem Res. 2016 Dec 20;49(12):2746-2755. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00409. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Acc Chem Res. 2016. PMID: 27993009
-
Cyclodextrin-Based Synthesis and Host-Guest Chemistry of Plasmonic Nanogap Particles with Strong, Quantitative, and Highly Multiplexable Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Signals.J Phys Chem Lett. 2020 Oct 1;11(19):8358-8364. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c02624. Epub 2020 Sep 21. J Phys Chem Lett. 2020. PMID: 32956585
-
Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Multiplexed Raman Bio-Imaging of Surface Roughness-Controlled Nanobridged Nanogap Particles.Small. 2016 Sep;12(34):4726-34. doi: 10.1002/smll.201600289. Epub 2016 Mar 29. Small. 2016. PMID: 27028989
-
Recent advances in non-plasmonic surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy nanostructures for biomedical applications.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022 Jul;14(4):e1795. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1795. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35362261 Review.
-
Raman Scattering-Based Biosensing: New Prospects and Opportunities.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Dec 13;11(12):512. doi: 10.3390/bios11120512. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34940269 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Design of plasmonic nanomaterials for diagnostic spectrometry.Nanoscale Adv. 2018 Nov 23;1(2):459-469. doi: 10.1039/c8na00319j. eCollection 2019 Feb 12. Nanoscale Adv. 2018. PMID: 36132258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy for Biomedical Applications: Recent Advances and Future Challenges.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Mar 19;17(11):16287-16379. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c17502. Epub 2025 Feb 24. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 39991932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative Nanoplasmonics.ACS Cent Sci. 2018 Oct 24;4(10):1303-1314. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.8b00423. Epub 2018 Aug 29. ACS Cent Sci. 2018. PMID: 30410968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Facile synthesis of intra-nanogap enhanced Raman tags with different shapes.Nano Res. 2024 Sep;17(9):8415-8423. doi: 10.1007/s12274-024-6807-y. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Nano Res. 2024. PMID: 39439578
-
Plasmonic Photothermal Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019 Jul 22;6(17):1900471. doi: 10.1002/advs.201900471. eCollection 2019 Sep 4. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019. PMID: 31508273 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bao W.; Melli M.; Caselli N.; Riboli F.; Wiersma D. S.; Staffaroni M.; Choo H.; Ogletree D. F.; Aloni S.; Bokor J.; Cabrini S.; Intonti F.; Salmeron M. B.; Yablonovitch E.; Schuck P. J.; Weber-Bargioni A. Mapping local charge recombination heterogeneity by multidimensional nanospectroscopic imaging. Science 2012, 338, 1317–1321. 10.1126/science.1227977. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

