Cutaneous melanoma: From pathogenesis to therapy (Review)
- PMID: 29532857
- PMCID: PMC5843392
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4287
Cutaneous melanoma: From pathogenesis to therapy (Review)
Abstract
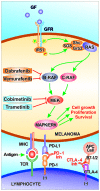
In less than 10 years, melanoma treatment has been revolutionized with the approval of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors, which have been shown to have a significant impact on the prognosis of patients with melanoma. The early steps of this transformation have taken place in research laboratories. The mitogen‑activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, phosphoinositol‑3‑kinase (PI3K) pathway promote the development of melanoma through numerous genomic alterations on different components of these pathways. Moreover, melanoma cells deeply interact with the tumor microenvironment and the immune system. This knowledge has led to the identification of novel therapeutic targets and treatment strategies. In this review, the epidemiological features of cutaneous melanoma along with the biological mechanisms involved in its development and progression are summarized. The current state‑of‑the‑art of advanced stage melanoma treatment strategies and the currently available evidence of the use of predictive and prognostic biomarkers are also discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
DAS is the Editor-in-Chief for the journal, but had no personal involvement in the reviewing process, or any influence in terms of adjudicating on the final decision, for this article. The remaining authors have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Rastrelli M, Tropea S, Rossi CR, Alaibac M. Melanoma: Epidemiology, risk factors, pathogenesis, diagnosis and classification. In Vivo. 2014;28:1005–1011. - PubMed
-
- Pennello G, Devesa S, Gail M. Association of surface ultraviolet B radiation levels with melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancer in United States blacks. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2000;9:291–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

