PEDF improves cardiac function in rats subjected to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting ROS generation via PEDF‑R
- PMID: 29532859
- PMCID: PMC5881792
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3552
PEDF improves cardiac function in rats subjected to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting ROS generation via PEDF‑R
Abstract
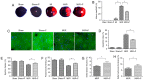
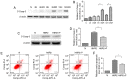
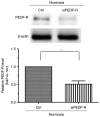
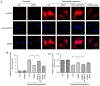
The prevention and management of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (MI/R) injury is an essential part of coronary heart disease surgery and is becoming a major clinical problem in the treatment of ischemic heart disease. Previous studies by our group have demonstrated that pigment epithelium‑derived factor (PEDF) improves cardiac function in rats with acute myocardial infarction and reduces hypoxia‑induced cell injury. However, the protective function and mechanisms underlying the effect of PEDF in MI/R injury remain to be fully understood. In the present study, the positive effect of PEDF in MI/R injury was confirmed by construction of the adult Sprague‑Dawley rat MI/R model. PEDF reduced myocardial infarct size and downregulated cardiomyocyte apoptosis in the I/R myocardium in this model. In addition, PEDF improved cardiac function and increased cardiac functional reserve in rats subjected to MI/R Injury. To further study the protective effect of PEDF and the underlying mechanisms in MI/R injury, a H9c2 cardiomyocyte hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) model was constructed. PEDF was confirmed to decrease H/R‑induced apoptosis in H9c2 cells, and this anti‑apoptotic function was abolished by pigment epithelium‑derived factor‑receptor (PEDF R) small interfering (si)RNA. Furthermore, administration of PEDF decreased the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and malondialdehyde (MDA) in H/R H9c2 cells. Compared with the H/R group, PEDF decreased mitochondrial ROS, increased the mitochondrial DNA copy number, reduced xanthine oxidase and NADPH oxidase activity, as well as RAC family small GTPase 1 protein expression. However, these effects of PEDF were markedly attenuated by PEDF‑R siRNA. To the best of our knowledge, the present study is the first to identify the protective effect of PEDF in MI/R injury, and confirm that the antioxidative effect PEDF occurred via inhibition of ROS generation via PEDF‑R under MI/R conditions.
Figures



References
-
- Damiani G, Salvatori E, Silvestrini G, Ivanova I, Bojovic L, Iodice L, Ricciardi W. Influence of socioeconomic factors on hospital readmissions for heart failure and acute myocardial infarction in patients 65 years and older: Evidence from a systematic review. Clin Interv Aging. 2015;10:237–245. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S71165. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

