Role of the EZH2/miR-200 axis in STAT3-mediated OSCC invasion
- PMID: 29532870
- PMCID: PMC5843395
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4293
Role of the EZH2/miR-200 axis in STAT3-mediated OSCC invasion
Erratum in
-
[Corrigendum] Role of the EZH2/miR‑200 axis in STAT3‑mediated OSCC invasion.Int J Oncol. 2023 Jul;63(1):80. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5528. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Int J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37264965 Free PMC article.
Retraction in
-
[Retracted] Role of the EZH2/miR‑200 axis in STAT3‑mediated OSCC invasion.Int J Oncol. 2025 May;66(5):34. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2025.5740. Epub 2025 Mar 21. Int J Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40116088 Free PMC article.
Abstract
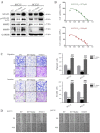
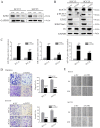
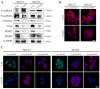
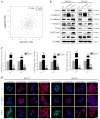
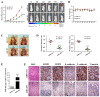
Abnormal activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) serves a pivotal role in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) tumor cell invasion into normal tissues or distant organs. However the downstream regulatory network of STAT3 signaling remains unclear. The present study aimed to investigate the potential mechanism underlying how STAT3 triggers enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) expression and inhibits microRNA (miR)-200a/b/429 expression in SCC25 and SCC15 cells in vitro and in vivo. Western blotting and reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction were performed to detect expression, and numerous functional tests were conducted to explore cancer metastasis. The results indicated that when STAT3 signaling activity was attenuated by Stattic or enhanced with a STAT3 plasmid, the EZH2/miR-200 axis was markedly altered, thus resulting in modulation of the invasion and migration of OSCC cell lines. In addition, loss of function of EZH2 compromised the oncogenic role of STAT3 in both cell lines. F-actin morphology and the expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers were also altered following disruption of the STAT3/EZH2/miR-200 axis. An orthotopic tumor model derived from SCC15 cells was used to confirm that targeting STAT3 or EZH2 suppressed OSCC invasion in vivo. In conclusion, the EZH2/miR-200 axis was revealed to mediate antitumor effects by targeting STAT3 signaling; these findings may provide a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of OSCC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Beasley NJ, Prevo R, Banerji S, Leek RD, Moore J, van Trappen P, Cox G, Harris AL, Jackson DG. Intratumoral lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res. 2002;62:1315–1320. - PubMed
-
- Patel V, Marsh CA, Dorsam RT, Mikelis CM, Masedunskas A, Amornphimoltham P, Nathan CA, Singh B, Weigert R, Molinolo AA, et al. Decreased lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis by mTOR inhibition in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res. 2011;71:7103–7112. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3192. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

